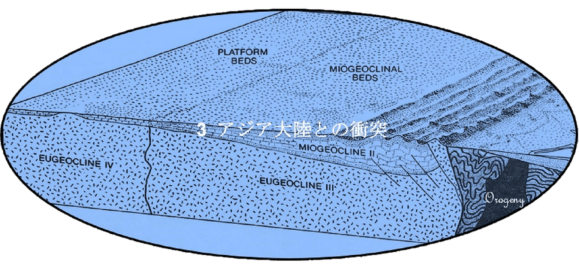
Collision with Asian Continent

Birth of Arabian Shield
(アラビア楯状地)
アラビア半島はアフリカ大陸の一部で、アラビア楯状地とヌビア楯状地は、同じ時代に同じ力で一体として形成されました。5千万年近く前までは分離してはなく、ゴンドワナ大陸の時代まで、テチス海でアジア大陸とアラビア半島は隔てられていました。アフリカ・アラビア・プレートがアジア大陸へと北東に漂い初めるに連れてテチス海は次第に狭められ、約5千万年前には両大陸の大陸棚が接触する程までに接近してアラビア湾(ペルシア湾)になりました。
In the past, the Arabian Peninsula was part of the African Continent. The Arabian Shield and the Nubian Shield were formed at the same time with the same force. It was the Arabian-Nubian Shield. It was not separated until nearly 50 million years ago. Until the time of the Gondwana, the Asian Continent and the Arabian Peninsula were separated by the Tethys Sea. The Tethys Sea was gradually narrowed as the African Plate (including the Arabian Peninsula) began to drift toward northeast to the Asian Continent. About 50 million years ago, it became the Arabian Gulf (the Persian Gulf) so close that the both continental shelves touched each other.

プレートを動かしている地殻深部の力によってアラビア半島はアジア大陸とますます接近し、接合して固く一体化しました。この過程で両大陸は、激しい圧力を受け、この接合面は高い山脈と成って隆起しました。この造山運動で出来たのがオマーンのハジャル山脈(アカダル山塊を含む)、イランのザグロス山脈やトルコの南東部のトウロス山脈(トロス山脈)です。それらの山脈の山頂部にはかっては海底であったことを示す海成石灰層が見られます。ザグロス山脈は、今日でも安定せずに地震が多発しています。
The deep crust forces that move the Tectonic Plate have made the Arabian Peninsula closer and closer to the Asian Continent, joining and tightly uniting. During this process, the two continents were under the intense pressure, and the junction surface were uplifted and became a high mountain range. The orogeny created the Hajar Mountains in Oman (including the Jebel Akhdar), The Zagros Mountains in Iran and the Taurus Mountains in the southeastern part of Turkey. The Marine Limestone Layers are found at the top of these mountains, which indicates that they were once the seafloors. The Zagros Mountains are still unstable and earthquake-prone.

6千万年前にアラビア半島西側の下部にある地殻は、引き延ばされ薄くなりました。地質構造としての結合が弱まりターイフの東側のハダン熔岩地帯と北のヨルダンを結ぶ線に沿って幾つも断層を発達させました。この線に沿った土地は陥没し、湖の連続を作りました。これは曉新生(6,500~5,600万年前)の間に断層でつながった一続きの水路と成って北は地中海へ抜けていました。同じ様な地殻の薄くなる過程がそれから数千万年後に起き、更に異なる断層がもっと西側に形成されました。これはいわゆる東アフリカの大地溝帯の一部で、紅海南のマンダブ海峡を中央として三つの割れ目に発達しました。一つは東アフリカを抜けて南へと延び、もう一つはジブチから東に走りアデン湾を作り、三番目は北西に延び、現在の紅海を作りました。
Sixty million years ago, the crust at the bottom west of the Arabian Peninsula was stretched and thinned. The geological bond weakened and several faults developed along the line connecting the Harrat Hadan (east of Taif) and Jordan north. The land along this line collapsed and created a series of lakes. In the Palaeocene (65-56 million years ago), these formed a series of waterways connected by faults, leading north to the Mediterranean Sea. A similar crustal thinning process occurred tens of millions of years later, and even more different faults were formed further west. It is a part of the Great Rift Valley in the East Africa and has developed into three fissures centered on the Bab el Mandeb south of the Red Sea. One extended south through the East Africa, the other ran east from Djibouti to create the Gulf of Aden, and the third extended northwest to create what is now the Red Sea.

by Dr. A.B. Salman, Egypt
紅海断層は幅100キロで長さは2,000キロに及んでいます。断層の両側が離れると中央部が沈下するので、急峻な崖地の両側と広く比較的平らな中央部を持つ事になりました。最初、谷は海とつながる程は深くもありませんでしたが、一番深い部分には湖が連続していました。裂け目が広がる過程が進行するに連れて、北側が地中海に抜け、地中海の海水がこの窪みを南へと浸水しました。陸橋がジブチ付近で谷の南側をアフリカとつないでいました。従ってこの時点ではインド洋へと抜けてはいませんでした。
The Red Sea Rift was 100 kilometers wide and 2,000 kilometers long. Since the central part subsided when both sides of the fault were separated, it had a wide and relatively flat central part with both sides of the steep Escarpment. At first, the Red Sea Valley was not deep enough to connect to the sea, but the deepest part was a series of lakes. As the process of widening the rift progressed, the north side connected into The Mediterranean Sea, and the seawater of the Mediterranean Sea flooded the depression to the south. The African Continent and the Arabian Peninsula were tied by an isthmus near Djibouti. Therefore, at this time, the Red Sea Valley had not connect to the Indian Ocean.
更に、2,500万年前には。広い谷の底の中央部に二番目の裂け目が出来ました。その裂け目は、狭いけれども平均1,000mの深さを持ち、場所によっては、その溝の底床の深さは、海面下2,000mにも達しています。両方の側の地殻(アラビアプレートはアフリカプレート)は、初めて完全に切り離されたので、マントルの中味が地表へと噴出する出口ができました。同じく2,500万年前にアラビア半島も非常にゆっくりでとアフリカ大陸から反時計回りに回転を始めました。これは、1,000万年も続いた為にそれに連れて中央の深い溝も幅を広げました。ティハーマ海岸低地がサラワート山脈(ヒスマー山地からヒジャーズ山脈、アシール山脈やイエメン中央高地を含み、イエメン西部高地まで続く)の麓と接した場所にある谷の側面に沿って異なる種類のマグマが夥しく侵入し、古い岩盤に鉱脈や土手を作りました。この大陸分離はその後、速度を緩め1,500万年前には動きを止めました。
Moreover, 25 million years ago. A second rift was created in the center of the bottom of the wide valley. The second rift is narrow but has an average depth of 1,000 m, and in some places the depth of the ditch can reach as high as 2,000 m below the sea level. The crust on both the sides (the Arabian Plate and the African Plate) were completely separated for the first time. At that part, there were the exits where the contents of the mantle spouted to the surface of the Earth. Also 25 million years ago, the Arabian Peninsula began to rotate counterclockwise from the African Continent very slowly. This lasted for 10 million years, so the deep groove in the center also widened together. On the Red Sea side of the Arabian Peninsula, the Sarawat Mountains was uplifted. The Sarawat Mountains is a collective term for the Hisma Massif, the Hijaz Mountains (the Hejaz Mountains), the Asir Mountains, the Yemen Central Highlands and the Yemen Western Highlands, which run from north to south. Alongside that, a Red Sea coastal plain called the Tihamah was formed between the Sarawat Mountains and the Red Sea. The Tihamah is generally flat, but contains the small lava areas with bumps such as craters in places. Along the sides of the valleys at the foot of the Sarawat Mountains in the Tihamah, the different types of the Magma invaded abundantly, creating the veins and the banks in old rocks. This continental separation then slowed down and stopped moving 15 million years ago.

1,500万年前はアラビア・プレートの全厚がユーラシア大陸と隣接した時期でした。両方の隙間はそれ以上広がる事はありませんでしたが、代わりに地域全体が地殻に侵入したマグマで膨張し、上方に押し上げられました。紅海から内陸を南北方向に走って膨張した地殻に沿って連続して火山が、マグマを上へと吹き出そうとする圧力に耐え切れ無く成って噴火しました。この火山活動はこの1,000万年の間、多かれ少なかれ続いています。
Fifteen million years ago, the full thickness of the Arabian Plate was abutted against the Eurasia Continent. Meanwhile the gap between the Arabian Peninsula and the African Continent did not widen further. Instead, the entire area was inflated by the Magma that had invaded the crust and pushed upwards. A series of volcanoes did run inland of the Red Sea in the north-south direction. They were unable to withstand the pressure to blow the Magma upwards and erupted along the expanding crust. This volcanic activity had been more or less ongoing for the last 10 million years.
これらの火山は殆どの場合、円錐形で低く広く緩やかなスロープを持ち、底面積の広い楯状火山と呼ばれる型のものです。この様な形に成ったのは、噴出する熔岩が非常に流動性の高い玄武岩で簡単に火口や噴出口から流れ出し、遠く広い地域を被う大きな熔岩膜に拡がる為です。この玄武岩の熔岩膜はアラビア半島西部の15万平方キロもの地域を被い、アラビア半島で最も荒れ果てた大地を代表しています。一般的に熔岩が被う地域の呼称である熔岩地帯(ハラトあるいはハラ)は、南にある程、北の熔岩地帯よりも古いのですが、多くは何百万年もの間に玄武岩の層で幾重にも折り重なって被われてしまっています。
Most of these volcanoes are conical, low and wide, with a gentle slope, and of a type called a shield volcano with a large base area. The reason for this shape is that the erupting lava is a highly fluid basalt that easily flows out of the crater or spout and spreads over a large lava membrane that covers a distant and wide area. This basalt lava membrane covers an area of 150,000 square kilometers west of the Arabian Peninsula and represents the most desolate land of the Arabian Peninsula. The Lava Field (Harrat or Hara), which is generally the name of the area covered by lava, and is older in the south than in the north. Many have been covered with layers of Basalt that have been folded over millions of years.

ハイバル熔岩地帯に隠されていた「ユダヤ人の砦」。
Harrat Khaybar and Jewish fort isolated in it and found by Mr. Chales Daughty in 1876 ~ 1878.
紅海の幅拡張の第二期は約500万年前に始まりました。紅海中央の更に深い中央の溝は再び活性化し、浅い海や塩湖は相互に繋がり一体化して現在の紅海と成りました。スエズ地峡が隆起して紅海は地中海から切り離なされ、アデン湾とマンダブ海峡が沈下してインド洋と水路で結ばれました。同じ時期に崖地やその隣接地に新たな隆起が起きました。それがサラワート山脈を今日の高さに押し上げアラビア半島の西から東への傾きを更に増大させました。紅海の長手方向中央に沿った中央の深い溝は、再び分離を初めて500万年の間に海底は150kmにまで幅が開きました。余り有りそうには思えないにしろ、熔岩地帯の最終的な広がりは今でも続いています。
The second phase of the Red Sea expansion began about 5 million years ago. The deeper central ditch in the center of the Red Sea had been reactivated, and the shallow waters and salt lakes had been interconnected and integrated into what is now the Red Sea. The Isthmus of Suez was uplifted and the Red Sea was separated from the Mediterranean Sea. Meanwhile, the Gulf of Aden and the Bab el Mandeb sank and were connected to the Indian Ocean by a waterway. At the same time, new uplifts occurred on the cliffs and their adjacent areas. It pushed the Sarawat Mountains to today’s height, further increasing the west-east slope of the Arabian Peninsula. The deep groove in the center along the longitudinal center of the Red Sea was once again separated and the seafloor widened to 150 km during the first 5 million years. The final spread of the Lava Fields is still going on, though it doesn’t seem very likely.

Harrat Rahat at As Suwayrqiyan located West of Mahed Al Dhahab (Gold Mine)
マディーナとラービグの間を南北に広く被うラハート熔岩地帯は、北部の火口だけでもこの4,500年間に13回噴火し、一番最近の噴火は730年前に起きてその地震の揺れはマディーナに届き、玄武岩が熔けてドロドロした膜状の熔岩流がマディーナ市街地にも及びました。新石器時代の人々は住居跡を玄武岩質熔岩の表面に残しています。その住居跡には墓や古墳、ストーンサークルや壁等が含まれ、これらは最近の熔岩流の上には勿論無く、地質学者が「新石器時代の構築物を含む土地を横切る熔岩大地は、新石器時代より若い」と結論付ける論拠に成っています。熔岩地帯の活動に先立つ地域全体の隆起は、紅海谷の底も隆起させ、浅い海や塩湖に変えました。熱い亜熱帯の太陽の下ではこれらの水の蒸発率は高く、塩類や水溶性鉱物は海に流れ込む河川や水の流れに運ばれ沈殿し、谷底に厚い層に成って蓄積しました。紅海海底では新しい堆積物に成れば成る程、岩塩、石膏、蒸発岩等の蒸発塩層があり、場所によってはその厚さは3キロにも及んでいます。
Harrat Rahat, which stretches north-south between Madinah and Rabigh, has erupted 13 times in the last 4,500 years at the northern crater alone. The most recent eruption occurred 730 years ago, and not only did the quake reach Madinah, but also a film-like thickness of lava extended to downtown Madinah. The lava is the melted muddy Basalt. The Neolithic people left their dwellings on the surface of cooled basaltic lava. The ruins of the dwelling include tombs, burial mounds, stone circles and walls. These are, of course, not on the recent lava flows, and are the basis for geologists to conclude that “the lava ground that crosses the land, including the Neolithic structures, is younger than the Neolithic.” The entire region’s uplifted prior to the activity of the lava field also raised the bottom of the Red Sea Valley. This turned the Red Sea Valley into shallow waters and salt lakes. Under the hot subtropical sun, the evaporation rate of these waters was high, and salts and water-soluble minerals were carried by rivers and water streams that flew into the sea. Those minerals had settled, and accumulated in thick layers at the bottom of the Red Sea Valley. The newer sediments on the seafloor of the Red Sea Valley contains the more amount of the layer (deposit) of the Marine Evaporites. The Marine Evaporites include rock salt, gypsum, and others, and in some places the sedimentary thickness is as high as 3 km.