13 People’s Activities
自然環境
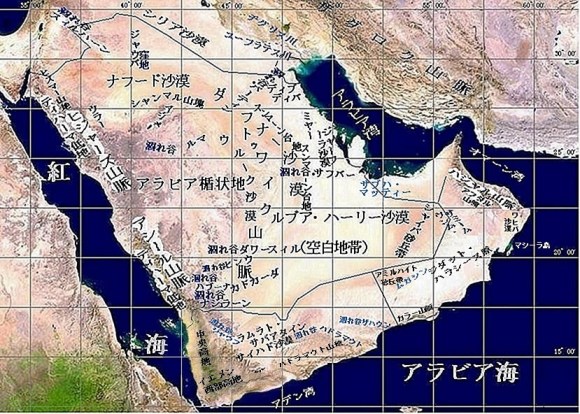
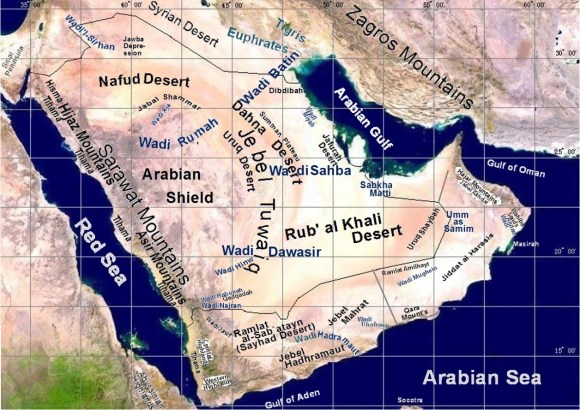
人々の営みは自然環境に大きな影響を与えます。アラビア半島は、海岸地帯とオアシス地帯を除けば、厳しく乾燥した気候です。その上に痩せて不毛に近い沙漠が広がり、水源や緑地はごく限られています。半島西部の紅海岸にはティハーマと呼ばれる細く長い平地が延び、その内陸側にサラワート山脈が並びます。サラワート山脈では、紅海から吹く風が山稜を超える時に湿気を雨として降らせます。そのため、ティハーマには流れのある涸れ谷も少なくありません。半島南部をイエメン西部山地からドファール山脈へと続く山並みとその前面の海岸地帯では湿潤な北西風の季節風の恩恵を受けています。半島東南部のハジャール山脈は西からはアラビア海の季節風、北東からはオマーン湾を渡ってくる北東からの貿易風を受けるため、降雨があります。特に270kmに渡って海岸沿いに延びるバーティナは、昔から肥沃な地として知られています。この他、半島内にはカティーフ、ホフーフやリーワー等の古代からの大きなオアシス地帯もあります。ともあれ、厳しく乾燥した気候が半島の大部分を占めるので、他の地域と比べて、この半島は、人々の営みから受ける自然環境への被害が大きいと、言えます。
Natural environment
People’s activities have a big impact on the natural environment. The Arabian Peninsula has a harsh and dry climate, with the exception of the coastal and oasis zones. The Desert near infertile and barren spreads on that, and the water source and the green space are very limited. On the Red Coast in the western Arabian Peninsula, a thin, long flatland called the Tihama Lowland extends, and the Sarawat Mountains line up on its inland side. The wet wind blows from the Red Sea. When this wind crosses the ridges of the Sarawat Mountains, its moisture becomes the rain on the western mountain side. As a result, there are not few wadies with a water flow in the Tihama Lowlands. The mountains and hills extend from the Yemen’s Western Highlands to the Dhofar Mountains along the southern coast of this Peninsula. The coastal areas on their sea-front receive the benefit of the dew and fog from the wet air of the southwestern monsoon. In the southeastern part of the Arabian Peninsula, winds are blowing from both the southwest and northeast. The southwesterly wind is a monsoon across the Arabian Sea, while the northeasterly wind is a trade wind across the Gulf of Oman. Thanks to these benefits, the Hajar Mountains have been rained and the Batina region has long been known as fertile land. The Batina region is located at the northeastern foot of the Hajar Mountains and stretches 270 km along the Gulf of Oman. In addition, there are large ancient oasis areas such as Qatif, Hofuf and Liwa on this Peninsula. In any case, the harsh and dry climate occupies most of this peninsula, therefore it can be said that this peninsula suffers more damage to its natural environment from people’s activities than other regions.
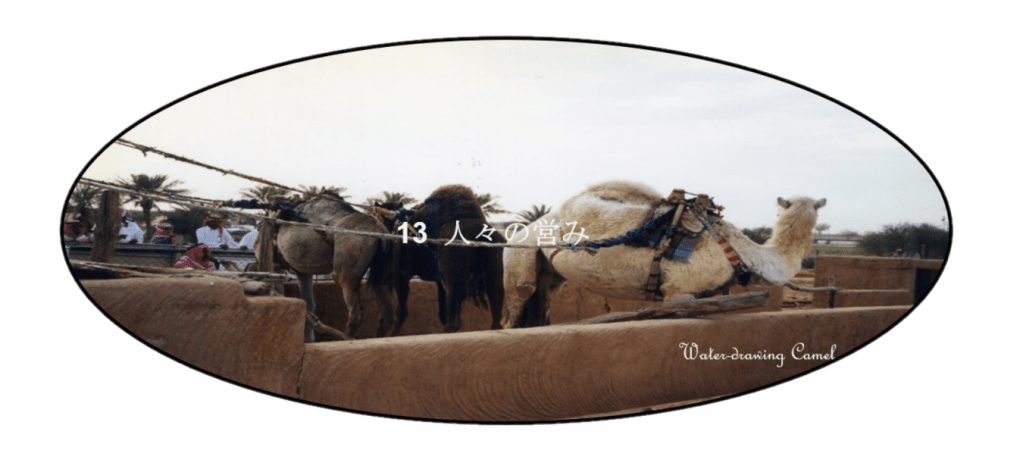
水
アラビア半島では降雨量を上回る水が蒸発します。この為に僅かな雨期を除けば、常に水不足の状態にあります。昔から降雨が地下に貯まった浅層水と共に、化石水とも深層水とも呼ばれる地層水が、掘り出し井戸の原理で、地上に湧き出している水を利用して来ました。
Water
In the Arabian Peninsula, more water evaporates than precipitation. For this reason, there is always a state of water shortage except for a slight rainy season. As water source in this Peninsula, deep water has been used together with shallow water from the ancient time. Deep water is the fossil water. Both deep and sallow water are rainfall which had accumulated underground. While deep water is ancient rain and is stored in deep strata for dozens thousand years, shallow water is recent rain, stored in shallow layer during relatively short period. While deep water springs out to ground by formation pressure through the well deeply excavated down to the stratum, shallow water naturally springs in an ordinary well or a fountain.

都市化と人口の増大で不足する水は、海水等の塩水を蒸留した造水で補ってきてます。アラビア湾岸のジュベールで造水した水を延々400キロ離れたリヤードまでパイプラインを使って、送水しています。また、紅海岸のシュカイクで造水した水を、標高差2,300メートルのアブハーまで揚水することまでも行われています。しかし、造水装置によって、濃縮された海水による塩分濃度が高まり、それによる環境への影響が既にあらわれてます。
Water, that is insufficient due to urbanization and population growth, is supplemented by freshwater produced from salt water, mostly seawater. Freshwater produced in Jubail on the Arabian Gulf Coast is fed via pipeline to Riyadh, 400 kilometers away. In addition, the freshwater, made by Shuqaiq water production plant on the Red Sea Coast, has been pumped up to Abha located at the altitude of 2,300 meters. Thus, the salt concentration has been increased by making greater water-production-facilities in size and number both in the Arabian Gulf Coast and the Red Sea Coast. Its influence has already appeared on the environment.

Sea water desalination plant in Al-Khobar, Jubail Seawater Reverse Osmosis Plant
陸上でも都市下水が処理されないままに、沙漠に放出されています。それが湖にも匹敵する水溜りを作り出しました。そこでは養魚場から逃げだしたテラピア等の外来生物が大量発生しています。また、衛生面で大きな環境問題を引き起こしてます。都市下水の再生処理化はかなり大規模に行われてもいます。その処理水は、涸れ谷等に流し込んで農業用水の補充水として利用されてます。それでも、処理水の量は、下水の放出量にとても追いついていません。
On land, urban sewage had been released into the Desert without being treated. It created a big puddle comparable to a lake. There, a large number of alien organisms such as Tilapia, which have fled from the fish farm, have occurred in large scale. In addition, it causes a big environmental problem in terms of hygiene. The recycling of urban sewage has been carried out on a fairly large scale. The treated water is poured into a wadi etc. and used as replenishment water for agricultural water. Still, the amount of treated water had been limited comparing with the amount of sewage released.
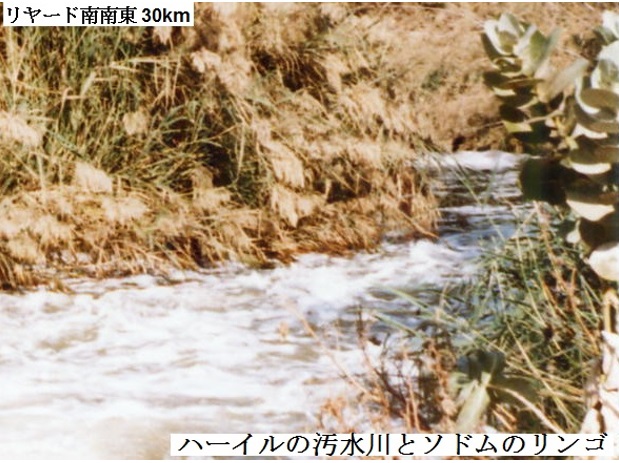


「水は沙漠に浸み込み吸収される」との誤解も少なくありません。沙漠は不浸透層が基盤にあるので、水を吸収しません。乾燥による蒸発によってのみ水が無くなります。この為に、水に溶け込んでいる塩分の集積が起こっています。塩分集積によって、沙漠の荒れ地化がさらに促進されています。塩分集積は、大規模散水型の円形農場でも起きています。上空からみると、塩分集積の為に廃棄された膨大な数の円形農場が、沙漠に累々と並んでます。
Many people misunderstand that water is easily absorbed by soaking into the Desert. The Desert does not absorb water because of the impervious layers on its base. Water is decreased and disappeared only by evaporation by drying. For this reason, salt dissolved in water has been accumulated on ground widely. The salt accumulation further accelerates the deteriorated wasteland of the desert. Salinity accumulation also occurs in large-scale of center pivot farms. A huge number of pivot farms have been discarded because of exceed salinity accumulation, and expose their circle wreckages in the Desert.

アラビア半島では1人当たり、「1日に400リットル以上の水を消費している」と、水の浪費が指摘がされてます。水供給にかかわる費用の大部分を政府が出費しているので、個人の負担が余りありません。このことも、貴重な水資源であるにもかかわらず、大量消費される原因と思われます。
In the Arabian Peninsula, the water wastage by human had also been pointed out. The water consumption per capita is more than 400 liters especially in urban areas. Since every government had been undertaken most of the costs related to water supply, it is not much burden on each individual. This is also one of causes of mass consumption, in spite of the preciousness of freshwater in this Peninsula.
原油とガス
1932年のバハレインを初めとして各地で石油発見が相次ぎました。1941年にアラムコ(現在のサウジアラムコ)が本格的に生産を始めました。
それからは、石油やガス収入によって、経済、建設、軍事、産業、教育等の社会生活が、他には例を見ない速度で、発展して来ています。その発展をもたらした膨大な費用は、大規模な石油・ガス関連事業からの歳入で、賄われてきました。
Crude Oil and Gas
Oil discovery was one after another in various places on the Arabian Peninsula including Bahrain in 1932. In 1941, ARAMCO (now Saudi ARAMCO) began full-scale production. It is that the social life such as economy, construction, military, industry, and the education, etc. has developed by the oil and the gas income at the speed which is unparalleled. The huge cost of this development has been covered by revenues from large-scale oil and gas-related businesses.


今でも石油・ガス関連事業が、アラビア半島各国の国内総生産の25%から56%を占めています。その反面、大型の石油・ガス生産処理出荷施設、製油所、石油化学コンビナート等から廃棄物や漏洩する石油や放出されるガスが、自然環境に悪影響を及ぼしています。それが油濁汚染や大気汚染を招いています。
Oil and gas-related businesses still account for 25% to 56% of the Arabian peninsula’s gross domestic product. On the other hand, waste, leaked oil, and released gas from large-scale oil and gas production and processing and shipping facilities, refineries, petrochemical complexes, etc. are adversely affecting the natural environment. This leads to oil pollution and air pollution.

特に1991年の湾岸戦争中に、イラク軍による原油の流出・放出(海上170万トン、陸上1,000万トン)および油田火災がありました。それらが、油濁および大気汚染に、もたらした甚大な被害は、今でもその影響を残しています。
In particular, during the Gulf War of 1991, the troop made huge oil spill by releasing intentionally a large amount of crude oil to environment (1.7 million tons at sea, 10 million tons on land) . And also, they set fire to major oil fields on an enormous scale. The enormous damage, causing the serious oil and air pollution, still has its effects in the northern Arabian Gulf.

植物と動物への影響
駱駝や羊を財産として保有する人達も少なくありません。多くの場合、人件費の安いスーダン人等の牧童に放牧させています。アラビア半島の75%地域が放牧可能です。しかしながら、飼育頭数は千数百万頭に及び、乾燥地帯で必要な1頭当たり20haを確保できずに、過放牧状態にあります。
Impact on plants and animals
Many people hold camels and sheep as property. In many cases, they are grazed to pastures under a cheap Sudanese livestock worker. 75% of the Arabian Peninsula is utilized as grazing land. Millions of animals are raised, however the number of breeding animals has already exceeded over the suitable level due to overgrazing. It cannot secure 20 ha per animal, which is the required pasture area in the arid zone.

また、かつては、沙漠に生える稀少な樹木を薪として商売する者もいました。流石に各州の知事が美観を理由に20世紀末までに禁止しました。
Moreover, people had logged rare and precious trees of Desert for firewood to sell for his business. The governor of each province had banned them by the end of the 20th century for desert beautification and environmental protection.
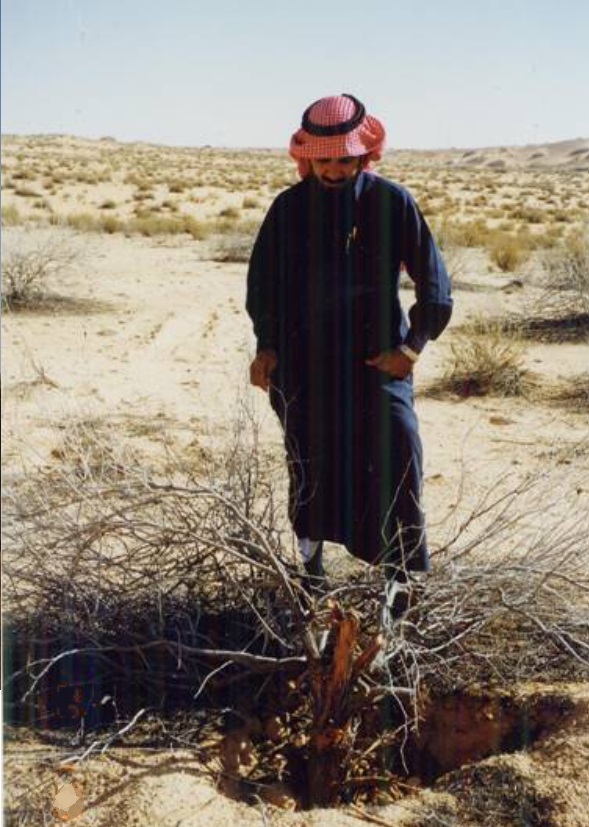


最近の問題は大規模に開催される沙漠ラリーです。これ等が野生の動物減少の大きな原因となっています。
最近の問題は大規模に開催される沙漠ラリーです。これ等が野生の動物減少の大きな原因となっています。

その上、住人が伝統的に狩猟を好み、狩猟動物は殆ど狩り尽くされた感があります。現在では野兎、狐やダッブと呼ばれる食用のトカゲ位しか獲物は残っていません。
In addition, inhabitants traditionally prefer hunting, and the animals for hunting preys have almost been eradicated. Today, only hares, foxes and Dhabb lizards survive as prey animals. Dhabb is also caught to sell for an edible animal in a market.

沿岸
遠浅海岸の続くアラビア湾でも、岸から深くなっている紅海でも、共にサンゴ礁が発達し、マングローブの群生が見られます。豊富な海洋生物が生息し、アフリカ大陸とユーラシア大陸を往来する渡り鳥の中継地となっています。南海岸ではさらに貿易風の影響を受けて降雨が期待できます。
Littoral
Generally, while the Arabian Gulf is shallow in depth, with gently sloped coast, the Red Sea is deep in depth, with steep sloped coast. In the both, Coral reefs are well developed and mangrove colonies can be seen. Each is home to an abundance of marine lives and serves as a transit point for migratory birds traveling between the African and Eurasian continents. On the southern coast of the peninsula, that are the Gulf of Aden and Arabian Sea, further rainfall can be expected because of monsoon and trade wind.


しかしながら、海岸線では、港湾化、原油積み出し港設置、工業都市化、海岸公園化、リゾート都市や住宅都市の建設で大きな環境変化が起きています。港湾化にはブービヤーン、シュアイバ、シュウェイク、ダンマーム、アブダビ、ドバイ、マスカット(スルターン・カーブース)、アデンやジェッダ等がります。原油積み出し港設置には、ミーナー・アル=アハマディー、ラアス・タヌーラ、ジュアイマ、メサイード(ムサイイード)、ジャベルダーナ、ダース島、フジャイラ、スハール、ラアス・マルカズ、アッシュ・シフル、ラアス・イサ等があります。経済都市や工業都市化にはジュベール、ジャバル・アリー、アブドゥッラー経済都市、ヤンブー等が挙げられます。
In spite of those natural beauties, many places of the coastal lines have already converted to harbors & ports, established crude oil loading ports, urbanized as industrial cities and changed to coastal parks. Major environmental changes are taking place because of them. Port cities include Bubiyan, Shuaiba, Shuwaikh, Dammam, Abu Dhabi , Dubai, Muscat (Sultan Qaboos), Aden and Jeddah, etc. Crude oil loading ports include Mina al Ahmadi, Ras Tanura, Juaymah, Mesaieed ( Musay’id)、Jebel Dhanna、Das Island、Fujairah、Suhar、Ras Markaz, Ash Shihr, Ras Isa, etc. Economic and industrial urbanization include Jubail, Jebel Ali, King Abdullah Economic City, Yanbu, etc.


ガスの有効利用
アラビア半島では人口当たりの土地面積が広いので大気汚染が生活環境上で意識されることは多くありませんでした。最大の大気汚染源は原油・ガスの生産に伴う随伴ガスの焼却でした。昔は、国際線の夜間飛行でアラビア半島に近づくと遠い彼方から空が炎で燃えているのが見える程でした。その様な随伴ガス焼却を禁止し、ガスの有効利用を図ってから既に数十年経っています。
Effective use of gas
Due to the large land area per capita on the Arabian Peninsula, air pollution was not often considered in the living environment. The largest source of air pollution was the incineration of accompanying gas, associated with the production of crude oil and gas. In the old days, when approaching the Arabian Peninsula on an international night flight, it was so visible that the sky was burning in flames from far away. It has already been decades since such accompanying gas was prohibited by the government to flare for disposing to atmosphere, and requested as well to utilize it for fuel gas both for domestic consumption and export goods.

現在の製油所、石油化学プラント、発電所、造水工場、自動車では大気汚染に対策しているので、問題は二酸化炭素の排出量だと、思われます。この対応として半島では風力や太陽光を利用した再生化のエネルギーの利用、原子力発電や電気自動車の導入が進められてます。
Air pollution had already been taken measures in the most of the recent industries, such as refineries, petrochemical plants, power plants, water plants, and various vehicles. Today, the major problem seems to be carbon dioxide emissions. In response to it, the governments of this Peninsula are promoting renewable energy using wind and solar power, and introducing nuclear power generation, electric vehicles, etc.


固形廃棄物処理
固形廃棄物処理は、昔は単に沙漠に放出していました。その後は沙漠に大きな穴を掘って埋めたり、積み上げて土を被せて人口の山を作ったりして処理してきました。例えばリヤード近郊のその様な山や穴は半端な大きさではありませんでした。大都市化と共にその様な場所の確保が難しいばかりが、有害成分の放出などの問題も出てきました。
Solid waste disposal
In the past, solid waste disposal was simply released into Desert. Afterwards, a big hole was dug in Desert, they were dumped and buried in it and covered it with soil, afterwards. Or, solid wastes were piled up on Desert and covered with soil to make artificial hill. For an example around Riyadh, such holes and hills are oddly large . Not only are such places unable to be secured with the expansion of urbanization, but also harmful substances, liquids and gases leak into the environment, which has become a major pollution problem.



