Caves on the Arabian Peninsula No.2

アラブ首長国連邦の洞窟
アラブ首長国連邦は、アラビア楯状地を取り巻き、石灰岩を主とする広大な堆積岩地帯でると共に、ハジャル山脈(Hajar Mountains)をその東部に含んでいます。しかし、横穴洞窟も陥没穴洞窟も大きな洞窟の発見が有望と思われますが、現在まで発見されている洞窟は、限られています。アブダビ登山クラブ(Abu Dhabi Alpine Club)などは、定常的にハジャル山脈(Hajar Mountains)での発見を試みています。勿論、専門家チームによる探索もこれまで何度か、行われています。最近では2022年6月にソロバキア(Slovenia) と アラブ首長国連邦大学(UAE University)の合同チームがムサンダムのオマーン国境近くのラアス・アル=ハイマ(Ras Al Khaimah)で探索してますが、発見には至りませんでした。この地域には「ラス・アル=ハイマ北部の山々にある夢の洞窟では、この世と平行した世界を占める超自然的な生き物であるジンの叫び声が鳴り響きます。」との民間伝承があり、有望に思えます。
現在のところ、アラブ首長国連邦の洞窟として挙げれているのは、ラス・アル・ハイマ洞窟(Cave in Ras Al Khaimah)とマガーラト・カシル・ハフィット(Magharet Qasir Hafeet)の二つで、それに小さいながら調査報告書のあるカーフ ・ハラット ・ナジェム洞窟(Kahf Kharrat Najem)です。それでも、著者は、「アラブ首長国連邦での大規模な洞窟の発見は、有望である」と期待しています。
Caves on the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates is located on the vast sedimentary rock band predominantly limestone surrounds around the Arabian Shield, and it also includes a part of the Hajar Mountains in its eastern side. Both side-hole caves and sinkhole caves seem promising to be found in large caves, however the caverns that have been discovered to date are limited. The Abu Dhabi Alpine Club and others are constantly trying to find a cave in the Hajar Mountains. Of course, there have been several rounds of exploration by a team of experts. Most recently, in June 2022, a joint team between Slovenia and UAE University explored the mountainous area in Ras Al Khaimah near the Omani border on the Peninsula, but they did not discover any caves. This area includes “a parallel world in Arab folklore, and such dream cave exists in the mountains north of Ras Al Khaimah. The screams of Jinn, the supernatural creatures, rings out in it. This is a folklore there, so a discovery of such cave seems promising.
Currently, there are two caves listed in the United Arab Emirates, Cave in Ras Al Khaimah and Magharet Qasir Hafeet. In addition, Kahf Kharrat Najem is a small cave but was investigated and reported.
The writer hopes that “the discovery of a large cave in the UAE.”
ハジャル山脈での洞窟の探索
ハジャル山脈のオマーン側には、いくつかの大きく壮観な横穴洞窟がありますが、UAE側では、未だに、そのような洞窟は、見つかっていません。時々は専門家が訪れて、探索もしているようですが、アブダビ登山クラブ(Abu Dhabi Alpine Club)等で、定常的に探索は行われています。装備の問題もありますが、温度、砂塵、コウモリなどの動物の糞尿等に加えて、高い崖の途中の横穴洞窟はアプローチが難しい等、様々な問題があります。それでも崖の麓や道路に近い場所にある洞窟を幾つか探検しています。
Explore the caves in the Hajar Mountains
On the Omani side of the Hajar Mountains, there are some large and spectacular side-hole caves, but on the UAE side, any of such caves have not been found, yet. Sometimes experts come and explore the area. The Abu Dhabi Alpine Club and others regularly search such caves in the Hajar Mountains in addition to that. There are a lot of problems not only apparatus, but also temperature, dust, manure of animals such as bats, etc. In addition, there are various difficulties such as approaching the side hole cave in the middle of a high cliff. Still, they can explore some of the caves at the foot of the cliffs and close to the road.

ラス・アル・ハイマ洞窟
涸れ谷ラフバ(Wadi Rahba)は、アラブ首長国連邦の最高峰ジャイス山(Jebel Jais)の西の山麓にある「スターダスト(the stardust climbing crag)」と呼ばれる岩登りのゲレンデに使われている谷です。ラス・アル・ハイマ洞窟は、そんな場所の奥にひっそりとあります。谷底の石造りの家(the heritage stone house)から洞窟の入口まで階段が設けられ、「千夜一夜物語」に述べれれている「アリ・ババの洞窟(the Cave of Ali Baba)」を彷彿とさせます。そこまでのアクセスは、四輪駆動車でも難しく途中からハイキング(hiking)する必要がありそうです。この谷のさら奥には昔からの泉もあります。なお、近年、ラフバ・ダム(Al Rahba dam)が下流に建設されたので、雨の後は通行できないと思われます。
Cave on Ras Al Khaimah
Wadi Rahba is a valley used for rock-climbing slopes called “the stardust climbing crag” at the western foothills of Mount Jebel Jais, the highest peak in the United Arab Emirates. La Cave in Ras Al Khaimah is tucked away in the depths of such a place. A staircase was provided from the Heritage Stone House at the bottom of the valley to the entrance to the cave, ” It is reminiscent of “the cave of Ali Baba” described in “A Thousand and One Nights”. Access to it is difficult even by four-wheel drive vehicle, and it seems that you need to hike from the middle. There is also an old spring further back in this valley. In recent years, Al Rahba dam has been built downstream, so it is expected to be impassable after rain.


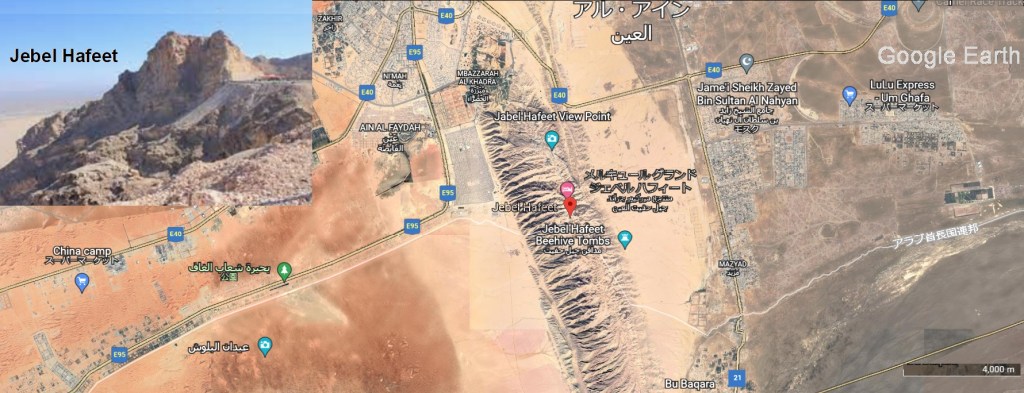
マガーラト・カシル・ハフート
アルアイン市の南に南北に長いハフィート山(Jebel Hafeet)があります。オマーンと共有され、両国の国境にまたがっています。ハジャル山脈(Hajar Mamuntains)の西にあり、独立していますが、その一部とされています。マガーラト・カシル・ハフート(Magharet Qasir Hafeet)はこの山中で一番大きな洞窟です。陥没孔洞窟で深さは、450メートルありますが、人間がはいれるのは深さ90メートルまでです。その中の部屋の一つのクリスタルボールルームは、立長さ15メートル、幅4メートルあります。部屋の内部には、石筍、鍾乳石、クリスタルがり、フローストーンやコラロイドで覆われています(flowstone, stalagmite, stalactites, crystals and coralloid coatings)。フローストーンの傾斜を登ると、ボールルームよりも小さいレッドルームに達します。ここでは上部のアルコーブ(床の間)は壮大な赤と白の垂直縞模様で古いフローストーンに切り取られています。これら2つの部屋の下と、入り口付近には水平洞窟が発達しています。マガレット・カシル・ハフィートが山の頂上で形成されたものではなく、それは通常の地下水によって形成され、非常に遅いプロセスで、地域のベースレベルの下で行われてたことを示唆しています。この洞窟は、一般には公開されていませんが、経験豊富な洞窟探検家だけがにはアクセスを許可されています。
Magharet Qasir Hafeet
To the south of Al Ain city, there is the long north-south Mount Jebel Hafeet. It is shared with Oman and straddles the border between the two countries. It is located west of the Hajar Mamuntains, and is independent but considered part of it. Magharet Qasir Hafeet is the largest cave in the mountain. This cave has a depth of 450 meters, however humans can only enter up to a depth of 90 meters. One of the rooms, the Crystal Ballroom, is 15 meters long and 4 meters wide. The interior of the room is covered with flowstone, stalagmite, stalactites, crystals and coralloid coatings. Climbing up the slope of the flowstone will bring to the Red Room, which is smaller than the Ballroom. Here the upper alcove (floor space) is cut into old flowstones with magnificent red and white vertical stripes. Below these two rooms and near the entrance, horizontal caves are developed. It suggests that the Magharet Qasir Hafeet was not formed at the top of the mountain, but that it was formed by ordinary groundwater and was done below the base level of this region, in a very slow process. This cave is not open to the public, but only experienced cavers are allowed access.
カーフ ・ハラット ・ナジェム洞窟
フジャイラ首長国(the Emirate of Fujairah)の北西部にある長さ35メートル、深さ10メートルの小さな洞窟ですが、乾燥した環境でのコウモリ尿素由来のミネラル(グアノ堆積物と黄色がかった鍾乳石)の研究のために調査されています。
Kahf Kharrat Najem
It is a small cave in the northwest part of the Emirate of Fujairah 35 meters long and 10 meters deep. It is being investigated for the study of minerals derived from bat urea in dry environments (guano deposits and yellowish stalactites).
オマーンの洞窟
オマーンは21世紀に入ってから観光開発に力を入れ、年間500万人の観光客が訪れる勢いです。洞窟探索も観光の基幹部門として整備されてきました。特にハジャール山脈ではカルスト地形探訪の重要な一部門を担っています。オマーン観光省は、まずフータ洞窟(Al Hoota Cave)を観光資源として整備し、続いて、2008年から世界で2番目に大きい洞窟と言われるマジュリス・ジン(Majlis al Jinn) の整備に取り掛かっています。また、涸れ谷バニー(Wadi Bani)のムカル洞窟(Muqal Cave)やシャルキーヤ地方(Ash Sharqiyah)のハーリド洞窟(Khalid)のように、観光客だけでもアクセスできる洞窟がありますが、他の洞窟にはかなりの努力、訓練、経験、特殊な設備が必要です。
Caves on Sultanate of Oman
Oman has been focusing on tourism development since the beginning of the 21st century, and it is attracting 5 million tourists a year. Cave sightseeing exploration has also been developed as a core part of tourism. Hajar Mountains in particular is an important part for tourism expl24oration of karst terrain. The Oman Ministry of Tourism first developed Al Hoota Cave as a tourism resource, and then they have been developing Majlis al Jinn cave as well, since 2008. Majlis al Jinn cave is said to be the second largest cave in the world. There are also caves that can be accessed by tourists alone, such as the Muqal Cave in Wadi Bani and the Khalid Cave in the Ash Sharqiyah Region, however considerable effort, training, experience and special equipment are Indispensable for visiting the other caves.
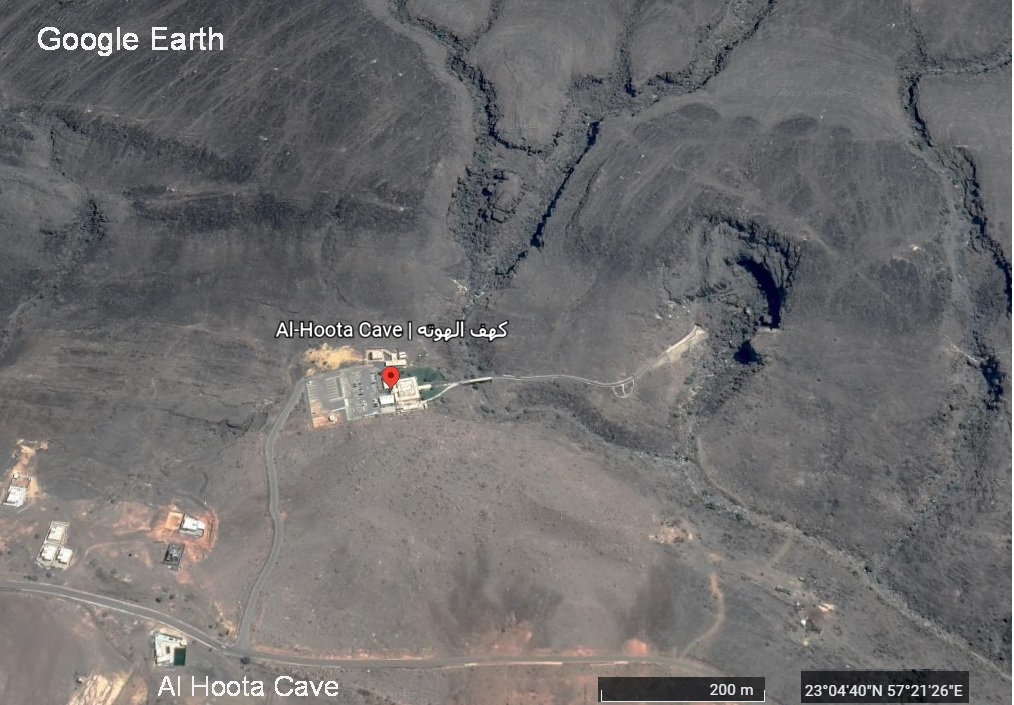
フータ洞窟
フータ洞窟(Al Hoota Cave)は、200万年前に形成され、シャムス山(Jabal Shams)(جبل شمس)の西の麓にある横穴洞窟です。シャムス山(Jabal Shams)は、ハジャル山脈(Hajar)の最高峰で「太陽の山」を意味し、標高は3,075メートルあります。
この洞窟は数百年前に地元の人々によって最初に発見され、さまざまな用途に使われてきました。全長は5キロメートルあり、内部は4つの湖で構成され、鍾乳石と石筍(stalactites and stalagmites)が良く発達して見事な景観を作り出しています。
4つの湖で構成されるフータ洞窟は、独特の生態系を持ち、さまざまな珍しい動物が生息しています。コウモリや節足動物から水カブトムシや軟体動物まで生息しています。特にフータ洞窟でしか見られない盲目の珍しい魚がいます。1980年に発見されましたが、地元の人々にブナセ(Bu Naseh)として知られていました。この魚はコイ科のガラバレイマイエ種(Garra barreimaie)に属し、洞内に数種類生息しています。完全に盲目で、透明な体をしています。
フータ洞窟(Al Hoota Cave)は、2006年12月に観光地として正式にオープンし、ビジターセンターからオマーン最初の電車に乗り、洞窟の奥の湖まで入れます。
Al Hoota Cave
Al Hoota Cave is a transverse cave formed 2 million years ago and located at the western foot of Jabal Shams (جبل شمس). Jabal Shams is the highest peak of the Hajar Mountains, meaning “Mountain of the Sun”, with an elevation of 3,075 m there.
The cave was first discovered by locals hundreds of years ago and has been used for a variety of purposes. It is 5 kilometers long and the interior consists of 4 lakes, with stalactites and stalagmites well developed to create a stunning landscape.
Consisting of four lakes, Futa Cave has a unique ecosystem and is home to a variety of rare animals. It inhabits everything from bats and arthropods to water beetles and mollusks. There are blind and rare fish, especially those that can only be seen in the Futa Caves. Discovered in 1980 but known to locals as Bu Naseh, this fish belongs to the Garra barreimaie species of the carp family and lives in several species in caves. Completely blind, has a transparent body.
Al Hoota Cave officially opened as a tourist destination in December 2006 and you can take the first train in Oman from the visitor centre to the lake at the innermost part of the cave.

ハバン洞窟
ハバン洞窟は、北シャルキーヤ行政区(Al Sharqiya North Governorate)のウィラヤト・ディッマ・タイイーン(Wilayat Dimma At Tayyin)東10キロにあります。洞窟は主に、さまざまな色の多くの岩層が存在することを特徴としています。
Abu Habban Cave
Abu Habban Cave is located 10 km to the east of “Wilayat Dimma At Tayyin” in “Al Sharqiya North Governorate”. The cave is mainly characterized by the presence of many rock formations of different colors.

マルニフ洞窟
この洞窟は、ドファル県(Dhofar Governorate) のサラーラ(Salalah)から約40キロ離れたシャッティアルムグセイル地区(Shatti Al Mughsayl)にあります。アラビア海の波が水中から岩の空洞を抜けて吹きあがるアルムグサイの吹き抜け(Al Mughsay blow holes)を見下ろす崖の上です。吹き抜けて噴出する水の音が豪快に感じられます。
Al Marnif Cave
The cave is located in Shatti Al Mughsayl, about 40 kilometers from Salalah in Dhofar Governorate. It is a clifftop overlooking the Al Mughsay blow holes, where the waves of the Arabian Sea blow up from the water through the rock cavities. The sound of water, gushing through the air, is lively exciting.

マジュリス・ジン洞窟
ハジャール山脈(Hajar Mountains)東部の麓で、マスカット県(Muscat Governorate)のウィラヤト・クライヤート(Wilayat Qurayyat)にあるフィンス村(Fins Village)の村の東に隠されているかの様にサルマ高原(Salma Plateau)があります。マジュリス・ジン(Majlis al Jinn)は、その高原上にあります。長さは310メートル、幅は225メートルです。ドーム型の天井が120メートルの高さで洞窟の上にあります。この洞窟は、その巨大さで世界最大の地下洞窟の1つと見なされてます。洞窟の規模の割には、開口部は3ヵ所だけです。この洞窟に降りるには、ロープを使うこと唯一の方法ですが、観光名所として整備されれば、エレベータなどの設備が備えられるでしょう。
Majlis Al Jinn Cave
As if hidden in the eastern foothills of the Hajar Mountains, east of the village of Fins Village at Wilayat Qurayyat in Muscat Governorate. There is the Salma Plateau. Majlis Al Jinn Cave is located on its plateau. It is 310 m long and 225m wide. A domed ceiling is above the cave at a height of 120 meters. This cave is considered one of the largest underground caves in the world for its enormity. Compared to the size of the cave, there are only three openings. The only way to get down to this cave is to use a rope, but if it is maintained as a tourist attraction, it is required to equipped with facilities such as elevators.


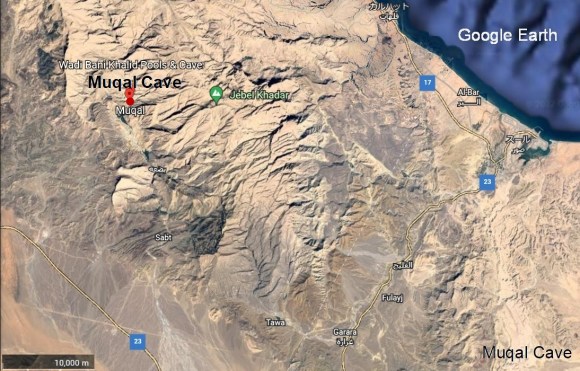
ムガル洞窟
この洞窟は、Al Sharqiya North GovernorateのWadi Bani Khalidにあり、有名な水たまりMuqal Water Poolsの近くにあります。洞窟に入ると、その固い岩を流れる地下水の大きな音がします。洞内には美しい岩の形成されています。アプローチのWadi Muqalに沿って流れる水たまりや小川も目を楽しませてくれます。
Muqal Cave
The cave is located at Wadi Bani Khalid in Al Sharqiya North Governorate, near the famous Muqal Water Pools. Upon entering the cave, the loud sound of groundwater flowing resonates through its hard rocks. Inside the cave, there are beautiful rock formations. Puddles and streams that flow along the Wadi Muqal approach are also pleasing to the eye.

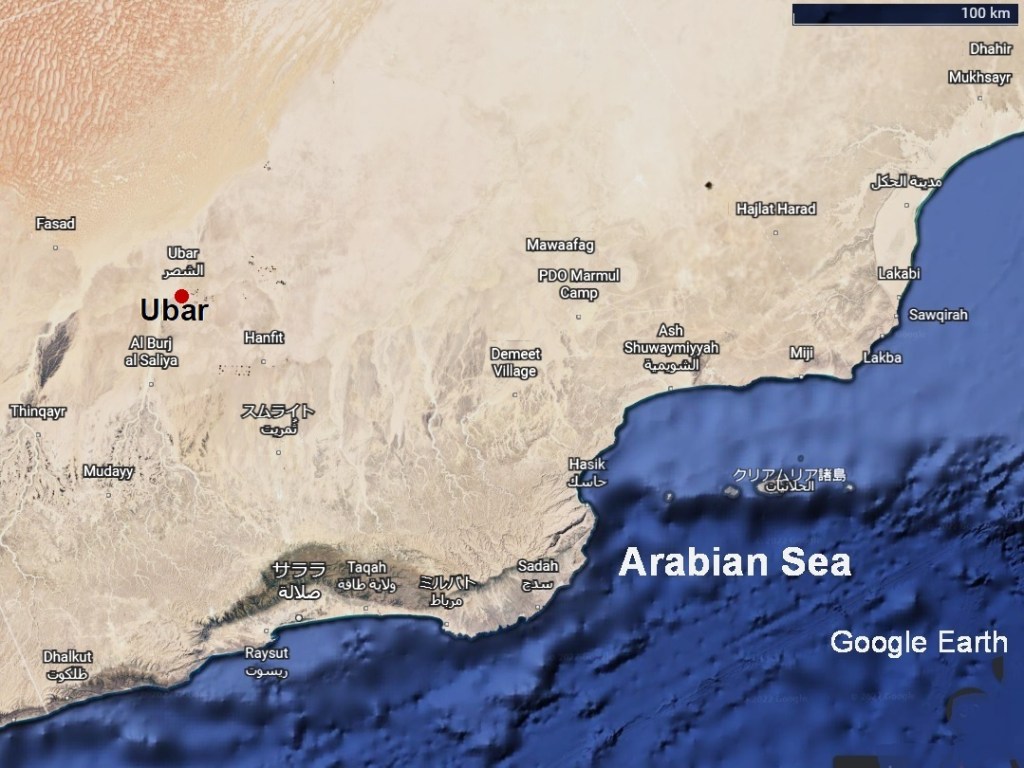
ウバールの洞窟
Ubarとは、旧約聖書に書かれている「千本柱の都市City of a Thousand Pillars、Iram of the Pillars or Wabar)」です。この都市はアラビア半島南部の空白地帯沙漠Rub al Khali Desertにありました。紀元前3000年から1世紀頃まで交易の中心として繁栄してながら、歴史の中に忽然として消えていまいました。そのため、「伝説の失われた都市」とも言われています。Qur’anでは「Noahの曾孫のアード Ad or A’adの一族が築いた町で、石の偶像神を崇拝する邪悪な人々が住んでいた。預言者Hudがこの町は頽廃され、繁栄を維持できなくなったことを警告した。アード (Ad)の息子で王であったシャッダド(Shaddad)は、これを無視し、反抗した。この為、神はこの町を滅ぼし、砂の中に埋めてしまわれた」と書かれているそうです。シャッダド(Shaddad)についての出来事はアラビアンナイト(Book of One Thousand and One Nights)の中でも語られています。この「伝説の失われた都市」を探す為に1980年代からナサの衛星写真(NASA Remote Sensing Images)等を使って乳香の道(Frankincense Route)を解析し、オマーン(Oman)のズファール地方(Dhofar)にこの「伝説の失われた都市」の所在の可能性を見出しました。1992年にラヌルフ・ファインズ(Ranulph Fiennes)、ジュリス・ザーリンス(Juris Zarins)等からなるアメリカ調査団がシスル(Ash Shisar or Ash Shisr)と云う泉の傍で、その水源となった鍾乳洞の中で、建造物を発見しました。ここは、16世紀にシス’ル砦(Shis’r)のあった場所で、300年から500年の間に大きな鍾乳洞陥没によって埋没していました。ここが、ほぼ、ウバール(Ubar)だと特定されています。
Cave of Ubar
The Ubar is the Old Testament definition of “City of a Thousand Pillars, Iram of the Pillars (Wabar).” The city was located in the Rub al Khali Desert in the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula. From 3,000 BC to about the 1st century BC it prospered as a trading center, but it disappeared abruptly in history. It is said that Ubar is written in the Qur’an as follows; “Ubar was a town built by the Ad (A’ad) clan of Noah’s great-grandchildren, and was inhabited by evil people who worshiped the stone idol god. Prophet Hud warned that they could no longer maintain their prosperity. King Shaddad ignored it and rebelled God, so God destroyed the city and buried it in the sand. (King Shaddad is Ad’s son.)” The events of Shaddad are also told in “Book of One Thousand and One Nights” to find this “legendary lost city”. In order to find this “legendary lost city”, the “Frank incense Route” was analyzed using NASA satellite images (NASA Remote Sensing Images) from the 1980s. As a result, the possibility of the location of this “legendary lost city” was discovered in the Dhofar region of Oman. In 1992, an American research team consisting of Ranulph Fiennes, Julis Zarins, etc. discovered a building near the water-spring called Ash Shisar (Ash Shisr) in the limestone cave. This is the water source of the said water-spring. It was the site of Fort Shis’r in the 16th century and was buried by a large limestone cave depression between 300 and 500 years. This is almost identified as Ubar.

イエメンの洞窟
イエメンは熔岩地帯と石灰岩を主とする堆積岩地帯が共にあるので、洞窟の潜在性は大きいと思います。現在、紹介されている洞窟はソコトラ島(Socotra)の洞窟とマフラ県 (Al Mahrah Governorate)にある「地獄の井戸」洞窟くらいですが、内戦が終われば、さまざまに発表があると思います。
Caves on Yemen
Yemen has both lava zones, and sedimentary rock zones mainly consisted of limestone, so the potential of caves will be great. Currently, the only caves that are featured are the caves of Socotra Governorate and the “Well of Hell” caves in Al Mahrah Governorate, but there will be various announcements once the civil war is over.
ソコトラ島の洞窟
ソコトラ島(Socotra)を中心とするソコトラ諸島は、アフリカの角から東に延びた大陸棚の上にあります。アラビア半島とは大地溝帯から分かれた海溝で隔てられています。この海溝は東北東に向かって延び、深度は2,500メートルに及びます。ソコトラ島(Socotra)は、地質的には基盤岩を覆う、幾層もの炭酸塩岩の層に覆われています。これらの炭酸塩岩層は、基礎となる白亜紀の石灰岩に三畳紀から中新世までの間に新たな炭酸塩岩層が次々と堆積して形成されました。カルスト化された白亜紀と第三紀の石灰岩には、数多くの洞窟が存在しますが、そのほとんどが調査されていません。長さやの大きさが様々な鍾乳石や石筍等の洞窟内鉱物堆積物(speleothem)形成されていますが、その多くが洞窟の底に落ちて、放置されたままです。これら地下洞窟の大部分は、より小さなオーバハングとトンネルで構成されています。また、人が降りて入って行ける大きな洞窟も少なくありません。さまざまな洞窟内には先史時代の人間から古代の船乗りの落書きまで考古学的な遺物も残されています。ここではホーク洞窟(Al-Hoq)とドグブ洞窟(Dogub Cave) の紹介にとどめます。
Caves of Socotra
Socotra Archipelago, the center of Socotra, sits on the continental shelf extending east from the Horn of Africa. It is separated from the Arabian Peninsula by the sea-trench split from the Great Rift Valley. The sea-trench extends east-northeastward and reaches a depth of 2,500 meters. Socotra is geologically covered by layers of carbonate rock that cover the bedrock. These carbonate rock formations were formed by the successive deposits of new carbonate rock formations during the Triassic to Miocene on the underlying Cretaceous limestone. Karstized Cretaceous and Tertiary limestone is home to numerous caves, most of which have not been investigated. Speleothems such as stalactites and stalagmites of varying lengths and sizes are formed, but their Many have fallen to the bottom of the cave and remain neglected. Most of these underground caverns consist of smaller overhangs and tunnels. In addition, there are not a few large caves that people can get down and enter. Inside the various caves are also archaeological artifacts ranging from prehistoric humans to graffiti of ancient sailors. Here, the introduction is limited for Al-Hoq Cave and Dogub Cave.

ホーク洞窟
ホーク洞窟(Al-Hoq)が一番大きく長さが3キロメートルにも及ぶ横穴洞窟です。ソコトラ島の北東部の断崖絶壁(precipice)に位置しています。そこには大きな花崗岩の塔のような壁が聳え、入り口はその壁の途中にあります。このため、登攀には2時間以上かかり、相当な冒険です。洞窟内は、人手が加えられてないので、照明も通路も手すりもなく、暗く冷たいばかりです。照明や装備は自前で整えなくてはなりません。洞窟は、石筍の聳える地底湖で終わっています。
Al-Hoq Cave
Al-Hoq Cave is the largest cave in Socotra, 3 kilometers long. It is located in the precipice in the northeastern part of Socotra. There is a large granite tower-like wall, and the cave entrance is in the middle of this wall. For this reason, the climb takes more than two hours and is quite an adventure. The inside of the cave is untouched, there are no lights, passages nor handrails, and it is only dark and cold. Lighting and equipment must be prepared by oneself. The cave ends with the stalagmites towering in front of the underground lake.

ドグブ洞窟
ドグブ洞窟(Dogub Cave)は、南部の海岸地帯を占めるノギッド平原(Nogid Plain)のほぼ中央にある横穴洞窟です。ディクサム高原(Diksam Plateau)の巨大な岩だらけの丘の麓にあります。その前面には美しい青い海を背景にハイフ、ザッハーク、ハルミ等のまばゆいばかりの白い砂丘(the white sand dunes of Hayf, Zahak and Halmi)が海岸線に沿ってうねるノギッド平原(Nogid Plain)が東西に延びていて、ドグブ洞窟(Dogub Cave)の存在は目立ちません。ねじれた石筍が大きな洞窟の口を守り、広大な内部は少なくとも20台の車を収容するのに十分な大きさです。洞窟の中で二股に分かれたいくつかの小さな部屋と滴る細い小川が、淡水の小さな自然の泉を作っています。ドグブ洞窟の水流は、多くの遊牧民だけではなく、コウモリやアマツバメ等の動物や鳥にとって、貴重な恵みです。ただ、ひどいコウモリの悪臭も洞窟の内部にまで浸透しています。
Dogub Cave
Dogub Cave is a side-hole cave is located almost in the middle of Nogid Plain, which occupies the southern coast. This location can be also said that it is the place at the foot of the huge rocky hill of the Diksam Plateau. In front of it, there are the dazzling white sand dunes of Hayf, Zahak and Halmi along the coastline against a backdrop of beautiful blue waters. The undulating Nogid Plain stretches from east to west, and the presence of the Dogub Cave is not noticeable. Twisted stalagmites guard the mouth of the large cave, and the vast interior is large enough to accommodate at least 20 cars. Several small rooms bifurcated in the cave and a narrow stream dripping create small springs of fresh water. The water stream in Dogub Cave is not only useful for many nomads, but also for animals and birds such as bats and swiftlets. It is a precious blessing. However, the terrible stench of bats has also permeated the interior of the cave.

バラフートの井戸
バラフート洞窟(Well of Barhout)は、イエメン本土のマフラ県 (Al Mahrah Governorate)のオマーン国境にあります。陥没穴洞窟(sink holl)で、直径は30メートルあり、深さは112メートルに達します。「多くの地元の人々は、巨大な穴が精霊の刑務所であり、冥界への玄関口である(a genie-infested gateway to the underworld)」と信じてきており、「悪名高い地獄の井戸(Well of Hell)」としても知られています。
2021年6月6日にオマーン洞窟探査チーム(Omani Caves Exploration Team(OCET))の10人の探検家のチームが、フランス通信社(AFP)と英国放送協会(BBC)の後援で、本格的な滑車システムを使用してバルフートの井戸を探検し、同年9月15日に底に達しています。
陥没穴洞窟の底は、石筍にで覆われ、ギザギザで、高さが9メートルもある石筍も含まています。床の一部は洞内真珠で覆われていました。
深さ65メートル付近の洞窟壁にある幾つかの穴からは水が湧き出し、小さな滝を作っています。この滴り落ちてくる水で石筍や洞窟真珠などの洞窟内生成物が形成されているようです。
また、ヘビ、カエル、カブトムシ、動物や鳥の死骸が見付かり、これらの腐敗した悪臭が洞内にこもり、「悪名高い地獄」とあだ名された所以だと思われます。但し、この探検の間にはそのような悪臭は有りませんでした。
陥没穴のでき方には崩壊型陥没穴(collapse sinkholes)と地盤沈下型陥没穴(subsidence sinkholes)の2通りがあります。崩壊型陥没穴は、表面下の岩盤の空隙が大きく膨張して上の屋根が支えられなくなり、岩とその上にある堆積物が突然洞窟に崩壊したときに形成されます。 一方、地盤沈下型陥没穴は、地表の堆積物がゆっくりと地下の小さな空隙に流れ落ち、大きな窪みまたは陥没穴が形成されます。地盤沈下型陥没穴は、鍾乳洞が典型と考えていましたが、原因が明確でない場合も多く、今後の研究が待たれます。
なお、詳細は、下記の記事を読んでください。
https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20210922-cavers-find-snakes-but-no-genies-in-yemen-s-well-of-hell
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/av/world-middle-east-58653795
Well of Barhout
Well of Barhout is located on the Oman border of Al Mahrah Governorate on the mainland of Yemen. It is a sinkhole cave, with a diameter of 30 meters and a depth of 112 meters. “Many locals have believed that the giant pit is a prison for spirits, a genie-infested gateway to the underworld,” and also known as the ‘Well of Hell’ .
On June 6, 2021, a team of 10 explorers from the Omani Caves Exploration Team (OCET) was launched under the auspices of the French News Agency (AFP) and the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) in a full-fledged. They explored the Well of Barhout using a pulley system and reached the bottom on September 15 of the same year.
The bottom of the cave is covered with jagged stalagmites, including stalagmites as high as 9 meters. Part of the floor was covered with cave pearls.
Water gushes out of several holes in the cave walls at a depth of about 65 meters, creating small waterfalls. It seems that cave products such as stalagmites and cave pearls are formed by this dripping water.
Carcasses of snakes, frogs, beetles, animals and birds were also found, and these putrid stenches may have been muffled in the caves, which is why they were nicknamed “Well of Hell”, however, there was no such stench during this expedition.
There are two ways to make Sink hole caves: collapse sinkholes and subsidence sinkholes. Collapse sinkholes are formed when voids in the bedrock below the surface expand so much that the roof above can no longer be supported, and the rocks and the sediments on top of them suddenly collapse into caves. Subsidence sinkholes, on the other hand, are where surface sediments slowly flow down into small underground voids, forming large depressions or sinkholes. Subsidence sinkholes were thought to be typical of stalactite caves, but the cause is often not clear, and future research is awaited.
For more details, please read the following article.
https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20210922-cavers-find-snakes-but-no-genies-in-yemen-s-well-of-hell
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/av/world-middle-east-58653795




