Dune zones in the Rub’ al Khali

ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の主な砂丘地帯
Main Dune Zones in the Rub’ al Khali
ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の主な砂丘地帯の一覧
List of Main Dune Zones in the Rub’ al Khali
| イルク・アブ・ハヤーラ | عرق أبو خيالة | The Irq Abu Khayalah |
| ウルーク・アワーリク | عروق الأوارك | The Uruq al Awarik |
| ウルーク・ザイザー | عروق الزيزي | The Uruq az Zayza |
| ウルーク・シャイバ | عروق الشيبة | The Uruq ash Shaybah |
| ウルーク・スユール | عروق السيول | The Uruq as-Suyul |
| ウルーク・バニー・ムアーリド | عروق ق بني معارد | The Uruq Bani Mu’arid |
| ウルーク・ヒーシャ | أورق الــهـيشة | The Uruq al Hishah |
| ウルク・マワーリド | أورق الموارد | The Uruq al Mawarid |
| ウルーク・ムウタリダ | العروق المعترضة | The Uruq al Mutaridah |
| ウルーク・ムーサ | عروق موسى | The Uruq Musa |
| ウルーク・ムライハ | عروق أبو مريخة | The Uruq abu Muraykhah |
| ウルーク・ムンダファン | عروق المندفن | The Uruq al Mundafan |
| ウルーク・ルマイラ | عروق الرميلة | The Uruq ar Rumaylah |
| ガニーム砂 | رمال غنيم | The Ghanim Sands |
| サナーム沙漠 | السنام | The As-Sanam Desert |
| シカト・ハリタ | شقة الخريطه | The Shiqat al Kharitah |
| ラムラト・ギルバニヤット | رملة الغربانيات | The Ramlat al Ghirbaniyat |
| ラムラト・クサイーブ | رملة الكثيب | The Ramlat al Kuthayyib |
| ラムラト・サフマ | رملة السحمة | The Ramlat as-Sahmah |
| ラムラット・ダフム | رملة دهم | The Ramlat Dahm |
| ラムラト・ミーターン | رملة ميتان | The Ramlat al Mitan |
| ラムラト・ファサド | رملة فسد | The Ramlat Fasad |
| リーワー地域 | ليوا | The Liwa area |
ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の主な砂丘地帯の位置地図
Location map for Main Dune Zones in the Rub’ al Khali
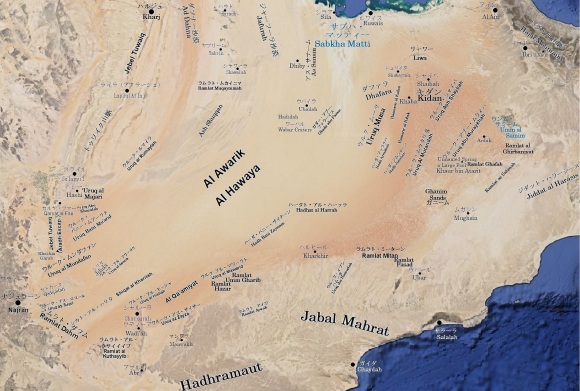
ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の主な砂丘地帯の説明
Descriptions for Main Dune Zones in the Rub’ al Khali
| イルク・アブ・ハヤーラ | The Irq Abu Khayalah |
| シャイーブ・ファーウから涸れ谷ヒンウが、涸れ谷ダワースィルへと連なる河床の南を、ほぼ平行に東西に並ぶ線形砂丘群です。 | It is a group of linear dunes that line up almost parallel to wadi running from the Sha’ib al Faw through the Wadi al Hinw to the Wadi al Dawasir. They occupy southern bank of the above wadi. |
| ウルーク・アワーリク | The Uruq al Awarik |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠で支配的な縦砂丘であるの線形砂丘から成るドラア級巨大ウルークの1つです。同沙漠の西南部にあり、ジリダの南に接しています。 | It is one of draa-class giant uruqs consisting of linear dunes, dominating in the Rub’ al Khali. It is bordering southern tip of Jilida in the southwestern Rub’ al Khali. |
| ウルーク・ザイザー | The Uruq az Zayza |
| ウルーク・ヒーシャを参照してください。 | See the Uruq al Hishah. |
| ウルーク・シャイバ | The Uruq ash Shaybah |
| ウルーク・シャイバーは現在のアラブ首長国連邦、サウジアラビアとオマーンとの国境のほぼ延長上を南南西へと百数十キロにわたって、ウンム・サミームの西側を延びる砂丘の山脈です。20世紀末最大の油田開発だった生産量50万 BPDのシャイバー油田はこの名に由来していると思われます。横砂丘であるメガバルハン砂嶺から成るドラア級のウルーク(大規模な砂丘山脈)をウルーク・ムウタリダやウルーク・ムライハと共に代表する砂丘に一つです。 | The border between Saudi Arabia and Oman extends south-southwest from border intersection of United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia and Oman. The Uruq ash Shaybah is along this border in west of the Umm al Samim, It is a mountainously big sand ridge that extends from south to southwest over a hundred and several tens of kilometers. It naming Shaybah seems to be derived from the Shaybah oil Field, which was the largest oil field development at the end of the 20th century and produced 500,000 ~ 1,000,000 BPD. It is one of representative dunes of draa-class uruq (large sand dune range) consisting of megabarchan ridges, which are barchanoid type dunes. The Uruq al Mutaridah and the Uruq abu Muraykhah are also megabarchan ridges same as the Uruq ash Shaybah. |
| ウルーク・スユール | The Uruq as-Suyul |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠南西部にあり、ナジュラーンとシャルーラを結ぶ道路のほぼ中間を東北東から西南西へと横切っています。同沙漠で支配的な縦砂丘であるの線形砂丘から成るドラア級巨大ウルークの1つです。 | Located in the southwestern Rub’ al Khali, it crosses at approximately midway point between Najran and Sharourah in direction from east-northeast to west-southwest. It is one of draa-class giant uruq consisting of linear dunes dominating in the Rub’ al Khali. |
| ウルーク・バニー・ムアーリド | The Uruq Bani Mu’arid |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠で支配的な縦砂丘であるの線形砂丘から成るドラア級巨大ウルークの1つです。セシジャーがシャイーブ・ファーウ(涸れ谷ヒンウ上流部)へと辿り着く前に越え、「南を向いた山脈の様に巨大な砂丘列」と呼んでいたバニー・マラドは、位置的にウルーク・バニー・ムアーリドです。現在では、世界最大の砂沙漠であるルブア・ハーリー沙漠の西端に位置する自然保護区に指定されており、Uruq Bani Ma’aridとして紹介されています。 | It is one of draa-class giant uruq consisting of linear dunes dominating in the Rub’ al Khali. The Bani Maradh, which Wilfred Thesiger crossed before reaching the Sha’ib al Faw and called it “a huge row of dunes like a mountain range, facing south,” is located in the present Uruq Bani Murid. Today, it is designated as a nature reserve located at western boundary of the Rub’ al Khali, and is introduced as the Uruq Bani Ma’arid (عروق بني معارض) by Saudi government. |
| ウルーク・ヒーシャ | The Uruq al Hishah |
| エドウィン・D・マッキー博士は、その報告書「世界の砂海の研究」中で、「ランドサット画像から特定した世界最大級の線形は、砂丘ルブア・ハーリー沙漠南西部のカアーミヤート地域にあり、個々のの線形砂丘は、幅は0.30〜2.7キロで延長190 キロに及ぶ」と紹介しています。これらには東北東からシャルーラ方面に連なるウルーク・アル・ヒーシャ を始め、ウルーク・アズ・ザイザーやウルク・アル・マワーリドが含まれると考えられます。 | Dr. Edwin D. Mckee wrote in his report “A Study of Global Sand Sea” that “the world’s largest linear dunes identified from Landsat imageries is the Al Qa’amiyat region in the southwestern Rub’ al Khali. The individual linear dunes ranges in width from 0.30 to 2.7 kilometers and extends 190 kilometers. ” These are thought to include the Uruq al Hishah, which runs from east-northeast to Sharourah, as well as the Uruq az Zayza and the Uruq al Mawarid. |
| ウルク・マワーリド | The Uruq al Mawarid |
| ウルーク・ヒーシャを参照してください。 | See the Uruq al Hishah. |
| ウルーク・ムウタリダ | The Uruq al Mutaridah |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠東南部のオマーン国境近くに北北東から南南西に横たわる砂丘地帯です。高さ230メートルまでの巨大な三日月形の砂丘が、広範囲にわたる内陸のサブカ基盤上に発達しています。横砂丘であるメガバルハン砂嶺から成るドラア級のウルーク(大規模な砂丘山脈)をウルーク・シャイバーやウルーク・ムライハと共に代表する砂丘に一つです。 ルブア・ハーリー沙漠のこの最東端は、冬は北北東から、夏は南西からの主な風が吹いています。 ウルーク・ムウタリダのいくつかの部分は、サブカ砂丘地域を囲む三日月形の要素を持つ魚の鱗のパターンを示しており、複雑な三日月形の尾根とも呼ばれています。 セシジャーは「南からの取りつきを生き生きとした緑の耐塩植物に縁取られた灰白色の石膏の平地から煉瓦色の個々に分かれた砂山が聳えている」と言っています。また、彼は砂丘間の含塩湿地を進んだとも書いています。 | Uruq lies from north-northeast to south-southwest near the Oman border in the southeastern Rub’al Khali. Huge crescent-shaped dunes up to 230 meters highly develop on an extensive inland Sabkha base. It is one of representative dunes of draa-class uruq consisting of megabarchan ridges (refer to the Uruq ash Shaybah for more details). The easternmost Rub’ al Khali has main winds from north-northeast in winter and from southwest in summer. Some parts of the Uruq al Mutaridah show a pattern of fish scales with crescent-shaped elements surrounding sabkha area, also known as complex crescent-shaped ridges. When Wilfred Thesiger first crosses the Rub’ al Khali 1946, he describes, prior to commence entering the area of draa-class uruq consisting of megabarchan ridges,” At first the dunes were separate mountains of brick-red sand, rising above ash-white gypsum flats (sabkhas) ringed with the vivid green of salt-bushes. Later they were even higher – five hundred feet or more (more than 150 meters) and honey-coloured.” After crossed the Uruq ash Shaybah he wrote that he went through sabkha (salt-containing wetlands) between dunes, then he also wrote “The colours of the sands were vivid, varied and unexpected, in places the colour of ground coffee, elsewhere brick-red, purple or a curious golden green”. |
| ウルーク・ムーサ | The Uruq Musa |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠東北部ダファラ地方のシュバイタ付近から南南西に延びる砂丘地帯です。この砂丘から東側にはドラア級の大きな横砂丘ウルークが並び、西側には比較的小規模の線形砂丘が並びます。 | The Uruq Musa is a sand dune area extending south-southwest from vicinity of Shubaytah in the Dhafara region of the northeastern Rub’ al Khali. On east of the Uruq Musa, large barchanoid type draa-class uruqs line up, while on west of the Uruq Musa relatively small linear dunes line up as well. |
| ウルーク・ムライハ | The Uruq abu Muraykhah |
| ウンム・サミームの西側に東北から南西に並ぶ線形砂丘地帯です。横砂丘であるメガバルハン砂嶺から成るドラア級のウルーク(大規模な砂丘山脈)をウルーク・シャイバーやウルーク・ムウタリダと共に代表する砂丘の一つです。 | The Uruq abu Muraykhah is a longitudinal dunes zone that runs from northeast to southwest on west of the Umm al Samim. It is one of representative dunes of draa-class uruq consisting of megabarchan ridges (refer to the Uruq ash Shaybah for more details). |
| ウルーク・ムンダファン | The Uruq al Mundafan |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠で支配的な縦砂丘であるの線形砂丘から成るドラア級巨大ウルーク(uruq)の1つです。南西部のハシュム・グラーブ南東70キロ付近を西南西から東北東に横たわっています。 | It is one of tdraa-class giant uruq consisting of linear dunes, which is dominant l in Rub ’al Khali. It lies from west-southwest to east-northeast around 70 kilometers southeast of Khashm Ghurab in the southwestern Rub’ al Khali. |
| ウルーク・ルマイラ | The Uruq ar Rumaylah |
| 涸れ谷ダワースィル東部を封じている砂丘地帯で、ダフナー沙漠南端のルブア・ハーリー沙漠内への延長部です。 | The Uruq ar Rumaylah approches to the Wadi al Dawasir region from northeastern. It is southern tip of extension part of the Ad Dahna into the Rub’ al Khali. |
| ガニーム砂 | The Ghanim Sands |
| 砂山砂丘の内の星形砂丘で、高さが100~200メートルを超える大きなものはアーホードともピラミッド砂丘とも呼ばれています。ルブア・ハーリー沙漠東部および東南部は、さらに東に聳えるハジャル山脈から大量の沖積層と砂利を供給されているので、砂丘は、大型です。 このため、風向きによって形成される星形砂丘もピラミッド砂丘になります。そのような、ピラミッド砂丘は南東縁部のラムラト・ミーターン、ラムラト・ファサド (およびガニーム・サンドなどに見られます。 その中では、セイシジャーが1946年10月に行った「第一回ルブア・ハーリー沙漠横断 」の入り口となったためもあり、ガニーム・サンドが特に知られています。セイシジャーは、ラムラット・ガファを超えて、ハウル・ビン・アタリート井戸でウルーク・シャイバー越えのための給水を行っています。この井戸の付近に現在は湧水湿地が出来ているそうです。 | Star-shaped dunes of sand mountains (isolated dune massifs, or qa’aid), larger than 100-200 meters in height, are called rhourd or pyramidal dunes. Dunes are generally large in the eastern and southeastern Rub’ al Khali, because large amounts of alluvium and gravel are supplied from the Hajar mountains, which rise further east. Accordingly, the star dunes formed by the wind direction in this area grow to pyramidal dunes. Such pyramidal dunes can be found mainly in the Ramlat al Mitan, the Ramlat Fasad and the Ramlat Ghanim on the southeastern margin of the Rub’ al Khali. Among them, the Ramlat Ghanim is particularly well-known, partly because it was the entrance to the “First Rub’ al Khali Crossing” conducted by Thesiger in October 1946. , Wilfred Thesiger crossed the Ramlat Ghafah. Then provided water for crossing the Uruq ash Shaybah at the Khaur-bin-Atarit well . It reported that a spring swamp is currently formed near this well by an NCWCD expedition to the eastern Rub’ al Khali in 1990. |
| サナーム沙漠 | The As-Sanam Desert |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠北西部にジャーフーラ沙漠から流れるが砂が大きく広がる砂丘地帯です。タリーズとも呼ばれ、ディビィ井戸、ウバイラ, ハディーダ, ワーバルを含む地域です。 H.スチュワート・エッジェル博士によれば、線形砂丘で、相互の間隔が1.5キロ、長さ5~30キロ規模のものが並びます。その中に特異な砂丘として、斜めの三日月形砂丘が見られ、見かけの卓越風向に対して斜めに延びています。 | In the northwestern Rub’al Khali, it is a dune area where sand flows from the Jafurah desert and spreads widely. This area is also known as Tara’iz al Sanam, and includes Dhiby well, Ubailah, the Umm al Hadidah and the Wabar Craters. According to Dr. H. Stewart Edgell, linear dunes are lined up with a distance of 1.5 kilometers and a length of 5 to 30 kilometers. As a peculiar sand dune, a diagonal crescent-shaped dune can be seen there, which extends diagonally with respect to apparent prevailing wind direction. |
| シカト・ハリタ | The Shiqat al Kharitah |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠南西部に並ぶ、同沙漠で支配的な縦砂丘であるの線形砂丘から成るドラア級巨大ウルークの1つです。 | It is one of draa-class giant uruq consisting of linear dunes, extending from east-northeast to west-southwest in northern Sharourah of the southwestern Rub Al Khali Desert. |
| ラムラト・ギルバニヤット | The Ramlat al Ghirbaniyat |
| ウンム・サミームの南にある砂丘地帯で、含塩平地中に比較的小規模なバルハン状砂丘の尾根が間隔を開けて、ほぼ東西に並んでいます。ウンム・サミーム南にあるバルハンの尾根と小さな個々のバルハンを伴う波状足首の砂丘群も含むと思われます。なお、セシジャーが1949年にこの砂丘の西側を通過しています。 | In the Ramlat al Ghirbaniyat south of the Umm al Samim, relatively small barchanoid ridges line up approximately east and west in sabkha (salt-containing plains). The Ramlat al Ghirbaniyat also includes barchanoid ridges south of the Umm al Samim and transverse wavy akle’ dunes with small individual barchan dunes. Wilfred Thesiger passed the west side of this dune in 1949. |
| ラムラト・クサイーブ | The Ramlat al Kuthayyib |
| ワディーアから西南西の延びる砂丘群です。1つの線形砂丘が北東に2つまたは3つの砂丘の尾根に分岐する発散砂丘が見られます。 | A group of dunes extending west-southwest from Wadi’ah in the southwestern Rub’ al Khali. There, we can see a divergent dune. That is one linear dune branches northeastward into two or three dune ridges. |
| ラムラト・サフマ | The Ramlat as-Sahmah |
| ウンム・サミームの南西のジダット・ハラーシース北西縁部にある砂丘で、最近ではSahmah517などのureilite Ramlatという希少隕石の発見と研究で注目されています。 | The Ramlat as-Sahmah is a sand dune on northwestern margin of the Jiddat al-Harasis and in southwest of the Umm al Samim. It has recently been noted for the discovery and research of rare meteorites such as Sahmah 517 called ureilite Ramlat. |
| ラムラット・ダフム | The Ramlat Dahm |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の南西の角から東南東へサウジアラビアのナジュラーン州とイエメンのジャウフ県の国境を挟んで、150キロにわたって延びています。標高は800メートルから1,000メートルで、ハドラマウト・アーチの一部でもあります。昔から乳香の交易路として使われ来ていますが、2001年8月にはこの砂丘を超えようとして14名が命を落としています。 | It extends 150 kilometers from southwest corner of the Rub’ al Khali to east-southeast along border between Najran province in Saudi Arabia and Al Jawf province in Yemen. It is also a part of the Hadramawt arch, of which altitude is 800 ~ 1,000 meters. It has been used as a frankincense trade route for a long time, yet in August 2001, 14 people died trying to cross this dune. |
| ラムラト・ミーターン | The Ramlat al Mitan |
| ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の南東部にある砂丘帯ラムラト・ミーターンでは、砂丘帯の南側には個々に分かれたピラミッド型の砂丘があり、砂丘帯本体は、高さ150メートル、直径2キロまでのピラミッド型の砂丘が、ほとんど結合した線形帯が幾つかほぼ平行に並んでいます。 Dr, H. S. Edgellは、ラムラト・ミーターンについて、その著書「Arabian Deserts: Nature, Origin and Evolution」で次の様に述べています。 「 アラビア半島の南部で典型的なのは、北東から南西に向かう冬の風ですが、その反対方向に向かうのが、夏の風です。この夏のモンスーン風は、ラムラト・ミーターン砂丘帯の形成にも影響を及ぼします。これらのバルハン砂丘の尾根の基本的なタイプは、対称的な三日月形の砂丘であるバルハン砂丘です。最も単純な形では、それらは鎌形であり、風下側に急な凹状の傾斜があり、風上側に緩やかな凸状の傾斜があります。このタイプの砂丘には、風下に面する2つの角または先端があります。多くの場合、バルハン砂丘は、より複雑な構造を持つ、より大きく複合的なバルハン砂丘として表示されます。この地域で見られる興味深い形は、クジラ型のバルハン砂丘です。三日月形は反対方向からの風によって変更されます。後部の傾斜は、従来のバルハンよりも急で、通常は10〜20°で、クジラの背中の典型的な形状を形成します。砂丘の尾根の間には、砂丘の砂利と石膏の平野があります。いくつかの場所では、それらは接続して、沙漠への長くアクセス可能な回廊を形成します。それらの床は通常、砂、泥、塩の固い組み合わせです。乾燥した平原を4×4の車で歩いたり、運転したりするのは簡単です。しかし、雨や鉄砲水の後、平野は浅い水層で満たされ、乾いて新しい地殻を形成するまで横断することはできません。地面が部分的に乾燥すると、柔らかい泥や中空の空洞の上に塩の地殻が形成され、地殻を突破した後、車両がスタックします。」 | The Ramlat al Mitan is located in the southeastern Rub’ al Khali, It is a dune belt consisted with a linear combination of pyramidal dunes up to 150 meters in height and 2 kilometers in diameter. Some linear belts are lined up almost in parallel with it. There are also individually separate pyramidal dunes on its south side. H. S. Edgell states in his book “Arabian Deserts” (excerpt): “In the southern Arabian Peninsula, a typical wind in winter is from northeast to southwest, but opposite direction is a summer wind which is monsoon. This summer wind affects the formation of the Ramlat al Mitan dunes. Typical barchanoid ridges are consisted of barchan dunes. A barchan dune is a symmetric crescent-shaped dune. In simplest form, a barchan dune is sickle shaped, and has a steep concave slope on downwind side. There are two horns or tips facing downwind. And also, there is a gentler convex slop on windward side. Often those barchan dunes are as larger, compound barchan dunes with more complex structures. An interesting shape seen in this area is a whaleback barchan dune. A certain crescentic form is transformed by wind from opposite direction. Its downwind slope is steeper than a conventional barchan, usually 10~20 °, and forms a typical shape of a whale’s back. Between barchanoid ridges, there are gravel and/or gypsum plains, etc. Those plains may connect each other to provide an easier approach to the Ramlat al Mitan. Its floor is usually a hard combination of sand, mud and salt. It’s easy to walk or drive a 4×4 car as a dry plain, but after a rain or a flash flood, this plain is filled with a shallow water layer. Then, it is unable to accessed nor go through. Even if a ground is partially dry, and a salt crust forms on soft mud or hollow cavities, vehicles frequently get stuck after breaking through these crusts. It cannot be traversed until it is completely dries to form a new crust.” |
| ラムラト・ファサド | The Ramlat Fasad |
| オマーンのドハール地方内陸のラムラト・ミーターンとウバールの間にあり、星形砂丘群で知られています。 | Located inland in the Dhofar region between Ramlat al Mitan and Ubar, it is known for its star-shaped dunes. |
| リーワー地域 | The Liwa area |
| リーワー地域は、アラブ首長国連邦の中央南部に位置し、ルブア・ハーリー沙漠の北東の風上縁に沿っており、約3,694平方キロをカバーしています。砂丘には1つのタイプがあります。それは、小さな砂丘が上に重なっていることを特徴とする、複合的で複雑な形のメガバルハンで、複合砂丘とも呼ばれます。バルハンの巨大なサイズのために、砂丘間の領域は、不規則な、細長い、三角形から円形または半円形まで形状が変化する閉じたくぼみとして表示されます。これらのくぼみは、ほとんどが小さなバルハンまたはサブカの堆積物で覆われており、上部に石膏(石膏で膠結された砂)のパッチがあります。バルハンとメガバルハンは、横方向に結合してバルハン状砂丘の尾根を形成することができ、リーワー地域では少なくとも70の砂丘の尾根が見られます。 | The Liwa area is located in the southern central United Arab Emirates, along the northeastern upwind edge of the Rub’ al Khali covering approximately 3,694 square kilometers There is a certain type of dune. It is a complex, complicate-shaped megabarchans, also known as a compound dune, characterized by overlapping small dunes. Because of its huge size as a barchan, an interdune area appears as a closed depression that changes shape from irregular, elongated, triangular to circular or semi-circular. These depressions are mostly covered with small barchans or sabkhas. A Sabkha has gypcrete (plaster-bonded sand) patches at its top. Barchans and megabarchans can be combined laterally to form barchanoid ridges. At least 70 such dune ridges can be found in the Liwa area. |