6 Aeolian Dunes Field of Arabian Peninsula

前書き
アラビア半島の現在の景観は、「5 地形の基盤と成る表層」で述べましたように、この半島の成り立ちを刻む火成岩系の花崗岩地帯と熔岩地帯、堆積岩系の砂岩地帯,と石灰岩地帯および風成された砂丘地帯の5つの地帯に分かれています。このうちで砂丘地帯の誕生は、極端に若いのが特徴的です。200万年位前から始まった氷河時代が終わりに近づいた頃、再び訪れた湿った時代(35,000~18,000年前)の後に、3,000年の間は、乾燥した時代が続きました。土壌は乾き、砂塵と成って卓越風向に沿って移動し、15,000年前までに、アラビア半島をおおう砂丘地帯が形成されました。
この時期に赤い砂は北のナフード沙漠から南のルブア・ハーリー沙漠へと主としてダフナー沙漠を通じて移動しています。その後、湿潤な気候は、9,000年前と4,500年前そして紀元前1,000年紀初めと紀元後1,000年年紀初めにも再来しています。しかしながら、基調としてはアラビア半島の乾燥は進み続けてきました。現在の砂丘地帯の景観は、極端に乾燥したここ数世紀の間に移動した砂で表面をおおわれています。
Preface
The current landscape of Arabian Peninsula is divided into five zones, as described in “5 Surface Layers forming Basis of Terrain”. Two of them are the igneous rock, which marks the origin of this peninsula, and there are the granite zone and the lava zone (harrat). Another two are the sedimentary rocks, the sandstone zone and the limestone zone. The remaining one is the aeolian sand dune zone.
Of these, the birth of the sand dune zone is characterized by being extremely young. Around the end of the ice age, which began about 2 million years ago, a dry era continued for 3,000 years after a revisited moist era (35,000 to 18,000 years ago). The soil dried, dusted and moved along the prevailing wind direction, forming a sand dune zone covering the Arabian Peninsula by 15,000 years ago.
During this period, red sand is moving from the Nafud al Kabir (hereinafter call An Nafud desert) in the north to the Rub’ al Khali desert in the south, mainly through the Ad Dahna desert. The humid climate has since reappeared 9,000 and 4,500 years ago and also in early 1,000 BC and early 1,000 BC. However, the basic trend is that the Arabian Peninsula has continued to dry out. The landscape of today’s sand dunes is covered with extremely dry sand that has moved over the last few centuries.
目次
Index
Other items included in this page:
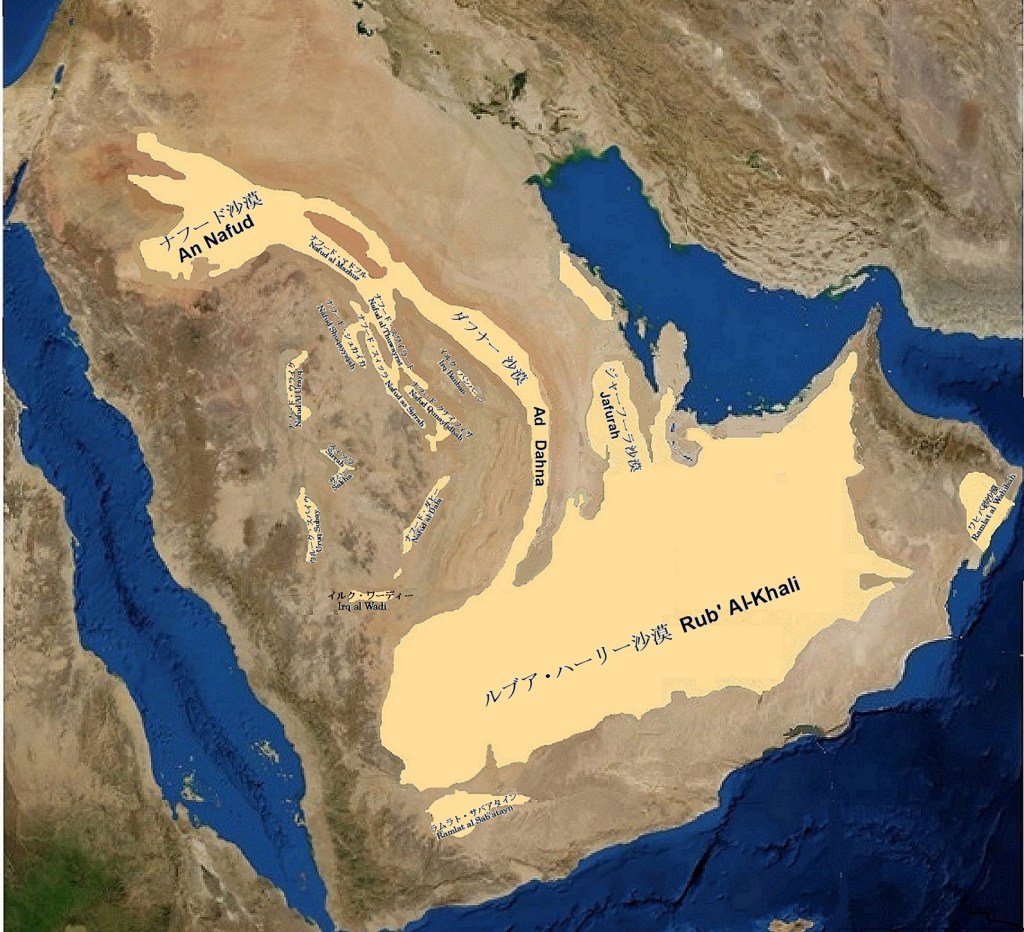
アラビア半島の風成砂丘地帯の地図
(Map of Aeolian Dunes Field of Arabian Peninsula)
概要
砂におおわれた面積は75万平方キロ以上にも及び、この半島の3分の1強に相当します。砂でおおわれている主要な場所は4つあります。
最も大きいのがルブア・ハーリー沙漠で、砂が55万平方キロを隙間無くおおっている世界最大の砂沙漠です。
北の偉大なナフード沙漠も大きく6万平方キロあります。
この二つの間に横たわっているのがダフナー沙漠で、1,000キロに及ぶ大きな弧型をして二つの砂の海を結んでいます。
これらとは全く別の砂の流れで、唯一白いジャーフーラ沙漠は、クウェートの南から始まり、ジュベール地域からハサー・オアシスの東を通り、南のルブア・ハーリー沙漠の間に横たわる移動する砂丘の塊でです。
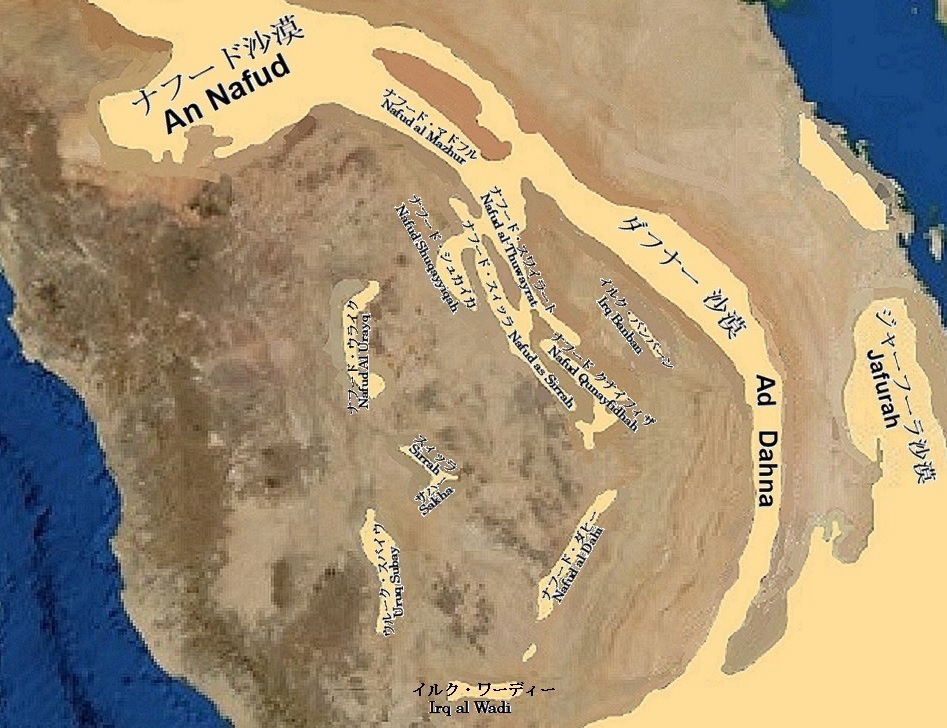
その他の砂丘地帯としては、ダフナー沙漠と同じように赤い砂をナフード沙漠方面からイルク・ワーディーを介して断続的に結んでいるウルーク沙漠とアラビア半島中央部をほぼ南北に間隔を置いて並ぶ小沙漠群があります。
前者がそれぞれナフードNafudと名付けられたナフード・マドフル、ナフード・スワイラート、ナフード・シュカイカ、ナフード・スィッル、ナフード・クナイフィザ、ナフード・ダヒーであり、私はイルク・バンバーンもこの中に加えても良いのではないかと思っています。
後者が、ウルーク・スバイウ、スィッラ砂丘帯、ナフード・ウライク、ナフード・サハー等です。
これらとは全く独立した砂丘地帯がアラビア半島南部のイエメンとオマーンにあり、それぞれがサイハド沙漠とワヒバ砂沙漠です。
もちろん、アラビア半島の至る所で小さな砂地が海岸から岩だらけの涸れ谷や山稜なの間など陸地の多くの場所にありますが、ここでは割愛しています。
Overview
The area covered with sand is more than 750,000 square kilometers, which is one-third of this peninsula. There are the four main places covered with sand.
The first is the Rub’ al Khali, the largest sand desert in the world with 550,000 square kilometers of sand covering it without gaps.
The second is the An Nafud in the north, which is 60,000 square kilometers.
The third is the Ad Dahna, which lies between the two and connects the two sandy seas in a large arc of 1,000 kilometers.
The fourth is a completely different stream of sand, the only white desert, the Jafurah. The Jafurah is a mass of moving dunes that begins south of Kuwait, passes through the Jubail region and the eastern region of the Al-Hasa oasis, and travels south until the Rub’ al Khali desert.
There are two other zones. Like the Ad Dahna, they also carry red sand intermittently from the An Nafud towards the Rub’ al Khali via the Irq al Wadi. They are the Uruq desert and the small desert group in the central region. The dunes that make up the former are named Nafud, respectively.
They are the Nafud al Mazhur, the Nafud al-Thuwayrat, the Nafud Ash Shuqayyiqah, the Nafud as Sirr, the Nafud Qunayfidhah, and the Nafud al-Dahi. (Note: I think the Irq Banban could be added to the Uruq desert.) On the other hand, the latter are the Uruq Subay, the Nafud as Sirrah, the Nafud Al Urayq, the Nafud as Sakha, etc. They are line up almost north-south, spaced in the central region of the Arabian Peninsula.
There are completely independent sand dunes in Yemen and Oman in the south of the Arabian Peninsula, respectively. They are the Sayhad desert (the Ramlat as Sab’atayn) and the Wahiba sand (the Ramlat al Wahibah).
Of course, everywhere in the Arabian Peninsula there are small sands in many parts of the land, from the coast to rocky wadi valleys and mountain ridges. They are omitted here due to space limitations.
アラビア半島中央部拡大図 (the Arabian Peninsula Central)
アラビア半島における砂沙漠の呼び方
砂沙漠の呼び方は、いろいろありますが、ここでは主なものを挙げておきます。砂沙漠は、漠々した砂の海というとらえ方をした呼び方のラムラト(رملة)と、砂の丘陵または細長い砂体というとらえ方した呼び方のウルーク(عروق)に分かれていると思っています。
ただ、ラムラト(رملة)の中のある部分をウルーク(عروق)と呼ぶことがあってもその反対ないようなので、呼び方としてラムラト(رملة)の方が砂沙漠の全体をイメージしていて、ウルーク(عروق)は、その中の一部分の呼び方のようです。
ラムラト(رملة)に近い呼び方としては、砂という意味のリマール(الرمال)があり、またナジュド(نجد)地方のラムラト(رملة)という意味のナフード(النفود)があります。その他、エルグ(إرغ)やサハラ(صحراء)が同じように使われていますが、これらは英語からの逆輸入で取り入れた呼び方のようです。
ウルー(عروق)には、縦砂丘のウルークと横砂丘のウルークがあります。縦砂丘のウルークでは砂丘列の方向と平行に並ぶ線砂丘が大半を占めています。
一方の横砂丘のウルークでは砂丘列の方向とほぼ直角に幾重にも並ぶ横断砂丘のウルークがそのほとんどです。
呼び方では縦砂丘と横砂丘の区別されていないようで、単にウルークと呼ばれています。単体の砂丘列の場合には、イルク(عرق)と呼ばれています。
この他の呼び方にはハード(حاذ)(整列)、ハーダト(حـاذة)(横列)、シカト(شقـة)(アパート)やハマーリール(حمـارير)(驢馬の群れ)が使われているようです。
Various names for the sand deserts in the Arabian Peninsula
There are many ways to call an sand dune, but here are the main ones. I think that the sand desert is divided into ramlat (رملة), which is called the vague sand sea, and uruq (عروق), which is called the sand ridge or elongated sand body.
However, even if a part of ramlat (رملة) is called uruq (عروق), there seems to be no opposite. Therefore, ramlat (رملة) has an image of the whole sand desert as a name, and uruq (عروق) seems to be a part of it.
A similar name to ramlat (رملة) is rimal (الرمال), which means sand. There is also nafud (النفود), which means ramlat (رملة) in the Najd (نجد) region. In addition, erg (إرغ) and sahara (صحراء) are used in the same way, but these are the names adopted by reimporting from English.
There are two types of uruq (عروق). One is uruq of the longitudinal dune and the another is uruq of the barchanoid type dune.
Most of the longitudinal dun uruq are “linear dunes” that line up parallel to the direction of the dunes. On the other hand, most of the barchanoid type dune uruqs are the barchanoid ridge uruqs that are lined up in layers almost at right angles to the direction of the dunes.
It seems that there is no distinction between the longitudinal dune and the barchanoid type dune in the name. It is simply called uruq. In the case of a single dune row, it is called Irq (عرق).
Other names seem to use hadh (حاذ) (alignment), hadhat (حـاذة) (row), shiqat (شقـة) (apartment) and hamarir (حمـارير) (donkey herd).
砂沙漠の構成
アラビア半島の特徴の一つは、広がったシート状や帯状の移動する砂で形成された砂沙漠です。砂沙漠といっても実際は、砂丘、砂丘間、砂シートt、および風成珪砕屑性サブカで構成されています。
砂丘間
砂丘の間は平坦から砂丘の間の緩やかに傾斜した領域です。だいたいの砂丘は砂丘間によって地形的に囲まれています。砂丘間では地下水面に近いので、塩分さえ多くなければ、植生が発達する可能性があります。
サンドシート
平らであるか、厚さ数メートルまでの平らな砂の板状した部分がサンドシートです。長い期間保たれる有効な風向と平行に水平方向に沿って、数メートルまたは数キロメートルも伸びることがあります。サンドシートの多くには植生があります。サンドシートを構成する砂は、周囲の砂丘よりも種類分けが不十分です。
サブハ
サブカは、含塩シルトで覆われた平地で、塩平原(ソルト・フラット)とも呼ばれます。塩分を多く含んだ浅い地下水面の存在に依存しているので、平坦で植生も無く、地質学的にも安定しています。水面が下がって、十分に乾燥していれば、大きな地耐力があり、大規模なものは宇宙開発用シャトルの着陸にも利用されている例もあります。しかし、水面が上昇して表面の塩が解かされると、一見、固そうに見えても人や動物までも嵌ってしまう流砂状態になってしまいます。このため、「毒の母」などとも呼ばれています。
Composition of sand desert
One of the characteristics of the Arabian Peninsula is an erg formed of spreading sheet-like or strip-shaped moving sand. The sand desert is actually composed of sand dune, interdune, sand sheet, and aeolian siliciclastic sabkha.
interdune
Between the dunes
Between the dunes is a gently sloping area between the flats and the dunes. That area is called the interdune. Most dunes are topographically surrounded by interdune. Since the interdune is close to the water table, vegetation can develop if there is not much salt.
sand sheet
A sand sheet is a flat or flat sand plate up to a few meters thick. It can extend several meters or kilometers along the horizontal direction parallel to the effective wind direction that is maintained for a long period of time. Many sand sheets have vegetation. The sand that makes up the sand sheet is less categorized than the surrounding dunes.
sabkha
sabkha is a flat land covered with salt-containing silt, also known as salt flat. It is flat, has no vegetation, and is geologically stable because it depends on the presence of a shallow water table that is high in salt. If the water surface is lowered and the surface of sabkha is sufficiently dry, it will have a large bearing capacity.
The large sabkha is also used for landing the space exploration shuttle. However, when the water level rises again and the salt on the surface is thawed, it becomes a quicksand state. Even if the surface looks hard at first glance, even humans and animals are fall in sabkha. For this reason, sabkha is sometimes referred to as the “mother of poison.”